Compare commits
10 Commits
0ba3236432
...
366bc6167a
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
366bc6167a | ||
|
|
ea49053e6c | ||
|
|
40e605ec48 | ||
|
|
c9cb7aa11d | ||
|
|
6758c73295 | ||
|
|
7cc090e1d7 | ||
|
|
7cc50ea1d2 | ||
|
|
b6b3929ecd | ||
|
|
44e69118c7 | ||
|
|
1dde3dc91f |
63
README.md
63
README.md
@ -10,6 +10,7 @@ Table of contents
|
||||
* [Introduction](#introduction)
|
||||
* [Description](#description)
|
||||
* [Getting Started](#getting-started)
|
||||
* [Limitations](#limitations)
|
||||
* [Possible Updates](#possible-updates)
|
||||
* [Sorting Algorithms](#sorting-algorithms)
|
||||
* [Bubble Sort](#bubble-sort)
|
||||
@ -23,6 +24,7 @@ Table of contents
|
||||
* [What is Big O Notation?](#what-is-big-o-notation)
|
||||
* [Time Complexity Notations](#time-complexity-notations)
|
||||
* [Table of Sorting Algorithms](#table-of-sorting-algorithms)
|
||||
* [Big O Complexity Chart](#big-o-complexity-chart)
|
||||
<!--te-->
|
||||
|
||||
Introduction
|
||||
@ -47,6 +49,12 @@ The four folders <strong>(sort_circle, sort_color, sort_combined, sort_scale)</s
|
||||
<li>Click the play button to run the script.</li>
|
||||
</ol>
|
||||
|
||||
## Limitations
|
||||
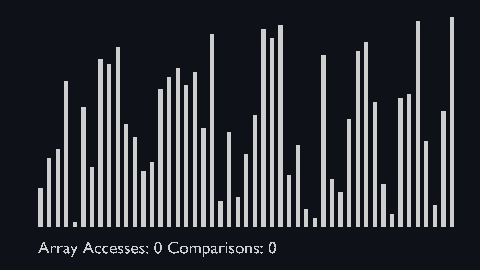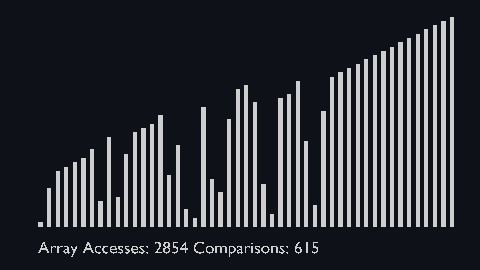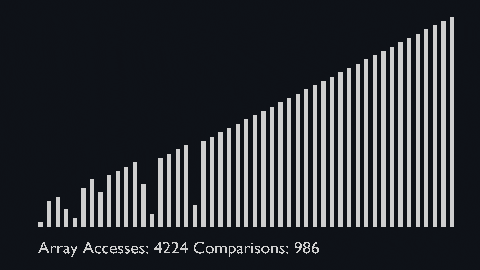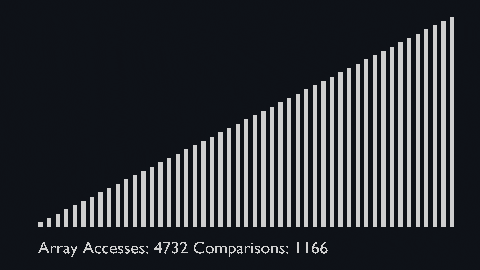
These visualizations don't show the efficiency of the algorithms.<br>
|
||||
They only visualize movement of the elements within the array.<br>
|
||||
But the array access and comparison counters are indicators of the time complexity of the algorithms.<br>
|
||||
For more information about the time complexity, you can take a look at the [Big O Table](#table-of-sorting-algorithms).<br>
|
||||
|
||||
## Possible Updates
|
||||
|
||||
Below I compiled a list of features that could be implemented in the future.
|
||||
@ -66,7 +74,6 @@ Below I compiled a list of features that could be implemented in the future.
|
||||
|
||||
<strong>Contributions to this project with either ideas from the list or your own are welcome.</strong>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
|
||||
Sorting Algorithms
|
||||
@ -74,8 +81,9 @@ Sorting Algorithms
|
||||
|
||||
|<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_combined/combined_sort_cube.py" target="_blank">combined_sort_cube.py</a>|
|
||||
| ------------- |
|
||||
|<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78089013/175064056-5a766e7b-2804-4ed6-b05d-786d26ebcbfb.gif" width="480" height="270">|
|
||||
||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Bubble Sort
|
||||
@ -89,10 +97,9 @@ Bubble sort is one of the most straightforward sorting algorithms, it makes mult
|
||||
In essence, each item “bubbles” up to the location where it belongs.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
| <a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_scale/bubble_sort_scale.py" target="_blank">bubble_sort_scale.py</a>|<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_color/bubble_sort_color.py" target="_blank">bubble_sort_color.py</a>|<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_circle/bubble_sort_circle.py" target="_blank">bubble_sort_circle.py</a>|
|
||||
| ------------- |-------------|-------------|
|
||||
| ||<img src="./img/bubble_circle.gif">|
|
||||
|
||||
| <a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_scale/bubble_sort_scale.py" target="_blank">bubble_sort_scale.py</a>|<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_color/bubble_sort_color.py" target="_blank">bubble_sort_color.py</a>|<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_circle/bubble_sort_color.py" target="_blank">bubble_sort_circle.py</a>|
|
||||
| ------------- |-------------|------------|
|
||||
|||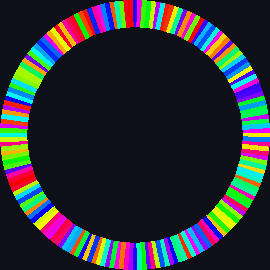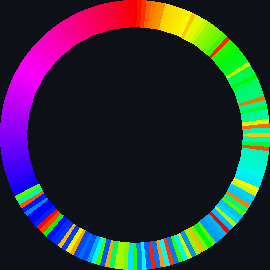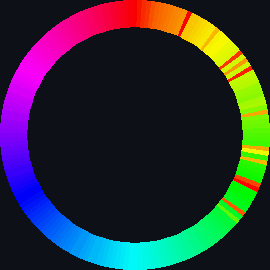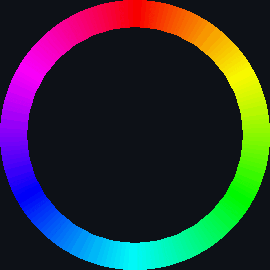|
|
||||
|
||||
## Insertion Sort
|
||||
|
||||
@ -108,20 +115,23 @@ then the values from the unsorted parts are picked and placed at the correct pos
|
||||
|
||||
| <a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_scale/insertion_sort_scale.py" target="_blank">insertion_sort_scale.py</a>|<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_color/insertion_sort_color.py" target="_blank">insertion_sort_color.py</a>|
|
||||
| ------------- |:-------------:|
|
||||
|||
|
||||
|||
|
||||
|
||||
## Selection Sort
|
||||
|
||||
The selection sort algorithm sorts an array by repeatedly finding the minimum element (considering ascending order) from unsorted part and putting it at the beginning.<br> The algorithm maintains two subarrays in a given array.
|
||||
The algorithm maintains two subarrays in a given array.
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>The subarray which is already sorted.</li>
|
||||
<li>Remaining subarray which is unsorted.</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
<p>In every iteration of selection sort, the minimum element (considering ascending order) from the unsorted subarray is picked and moved to the sorted subarray.</p>
|
||||
|
||||
|<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_scale/selection_sort_scale.py" target="_blank">selection_sort_scale.py</a>|<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_color/selection_sort_color.py" target="_blank">selection_sort_color.py</a>|
|
||||
| ------------- |:-------------:|
|
||||
|||
|
||||
|<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_scale/selection_sort_scale.py" target="_blank">selection_sort_scale.py</a>|<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_color/selection_sort_color.py" target="_blank">selection_sort_color.py</a>|<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_circle/selection_sort_circle.py" target="_blank">selection_sort_circle.py</a>|
|
||||
| ------------- |:-------------:|-------|
|
||||
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Heap Sort
|
||||
|
||||
@ -137,9 +147,8 @@ Heap sort basically recursively performs two main operations:
|
||||
|
||||
|<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_scale/heap_sort_scale.py" target="_blank">heap_sort_scale.py</a>|<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_color/heap_sort_color.py" target="_blank">heap_sort_color.py</a>|
|
||||
| ------------- |:-------------:|
|
||||
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|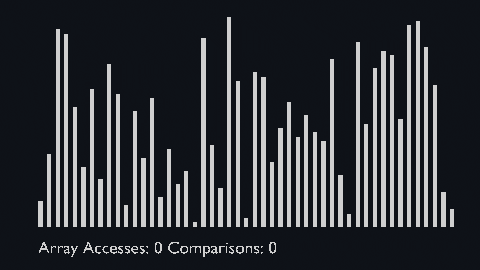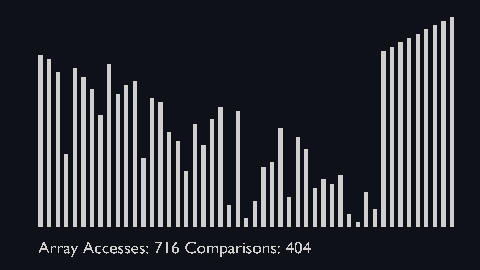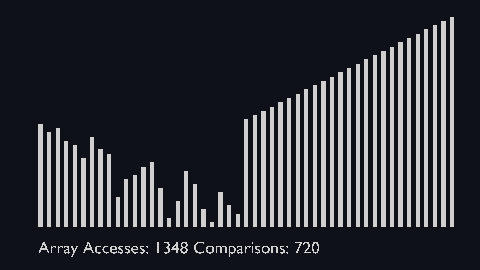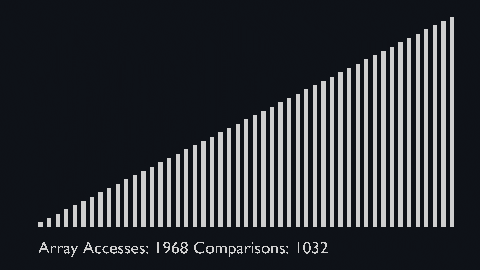||
|
||||
|
||||
## Shell Sort
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
The shell sort algorithm extends the insertion sort algorithm and is very efficient in sorting widely unsorted arrays.<br>
|
||||
@ -156,22 +165,20 @@ This sorting technique works by sorting elements in pairs, far away from each ot
|
||||
|
||||
|<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_scale/shell_sort_scale.py" target="_blank">shell_sort_scale.py</a>|<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_color/shell_sort_color.py" target="_blank">shell_sort_color.py</a>|
|
||||
| ------------- |:-------------:|
|
||||
|||
|
||||
|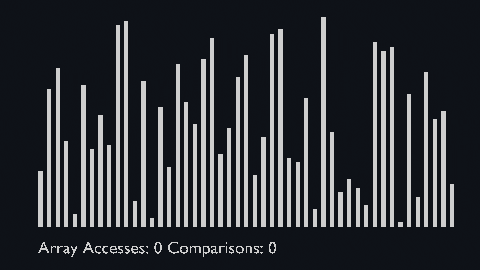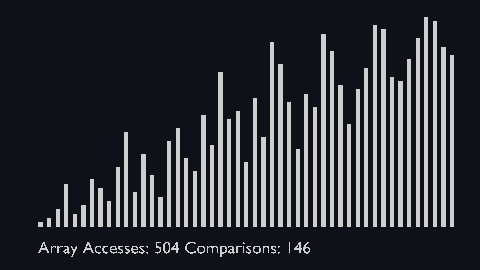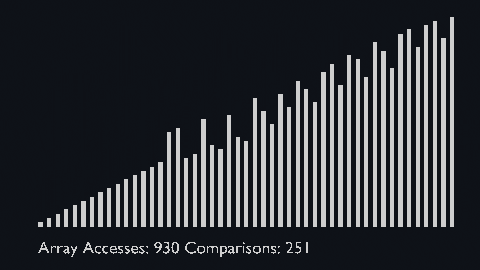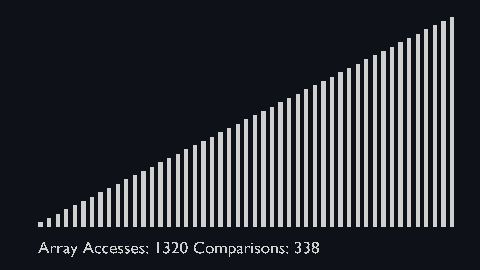|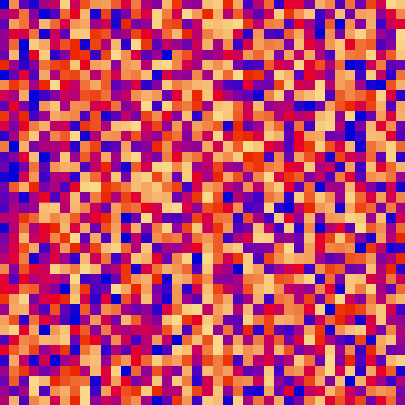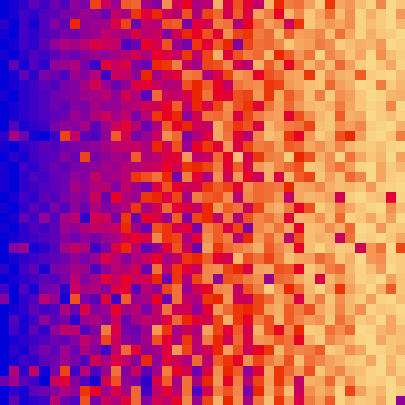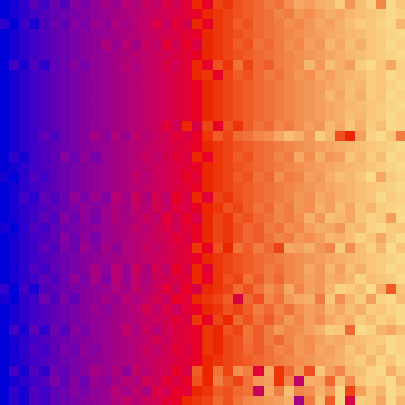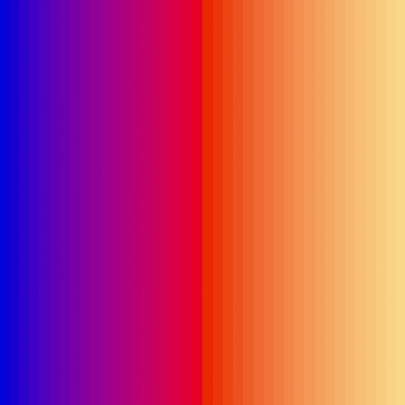|
|
||||
|
||||
## Merge Sort
|
||||
|
||||
Merge sort uses the divide and conquer approach to sort the elements. It is one of the most popular and efficient sorting algorithms.<br>
|
||||
It divides the given list into two equal halves, calls itself for the two halves and then merges the two sorted halves.<br>
|
||||
We have to define the <strong>merge()</strong> function to perform the merging.
|
||||
Merge sort uses the divide and conquer approach to sort the elements.<br>
|
||||
It is one of the most popular and efficient sorting algorithms.<br>
|
||||
|
||||
The sub-lists are divided again and again into halves until the list cannot be divided further.<br>
|
||||
Then we combine the pair of one element lists into two-element lists, sorting them in the process.<br>
|
||||
The sorted two-element pairs is merged into the four-element lists, and so on until we get the sorted list.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| <a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_scale/merge_sort_scale.py" target="_blank">merge_sort_scale.py</a>|<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_color/merge_sort_color.py" target="_blank">merge_sort_color.py</a>|
|
||||
| ------------- |:-------------:|
|
||||
|||
|
||||
| <a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_scale/merge_sort_scale.py" target="_blank">merge_sort_scale.py</a>|<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_color/merge_sort_color.py" target="_blank">merge_sort_color.py</a>|<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_circle/merge_sort_circle.py" target="_blank">merge_sort_circle.py</a>|
|
||||
| ------------- |:-------------:|------------|
|
||||
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Quick Sort
|
||||
|
||||
@ -187,9 +194,9 @@ Like Merge Sort, Quick Sort is a Divide and Conquer algorithm. It picks an eleme
|
||||
The key process in quickSort is <strong>partition()</strong>. Target of partitions is, given an array and an element x of array as pivot, put x at its correct position in sorted array and put all smaller elements (smaller than x) before x, and put all greater elements (greater than x) after x.<br>
|
||||
All this should be done in linear time.
|
||||
|
||||
| <a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_scale/quick_sort_scale.py" target="_blank">quick_sort_scale.py</a>|<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_color/quick_sort_color.py" target="_blank">quick_sort_color.py</a>|
|
||||
| ------------- |:-------------:|
|
||||
|||
|
||||
| <a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_scale/quick_sort_scale.py" target="_blank">quick_sort_scale.py</a>|<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_color/quick_sort_color.py" target="_blank">quick_sort_color.py</a>|<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_circle/quick_sort_circle.py" target="_blank">quick_sort_circle.py</a>|
|
||||
| ------------- |:-------------:|--------|
|
||||
|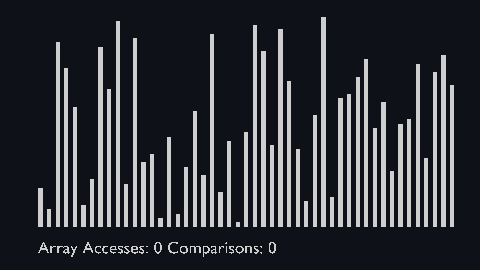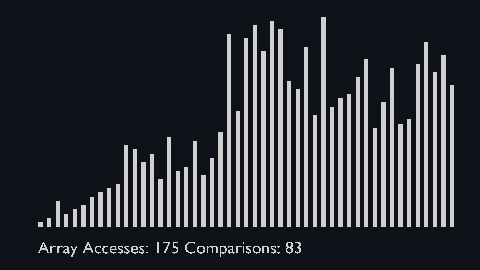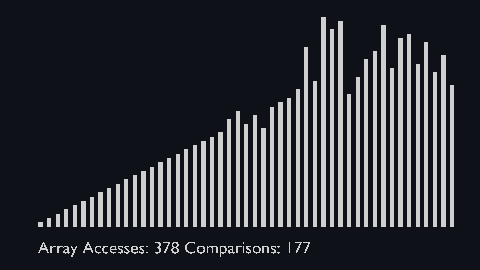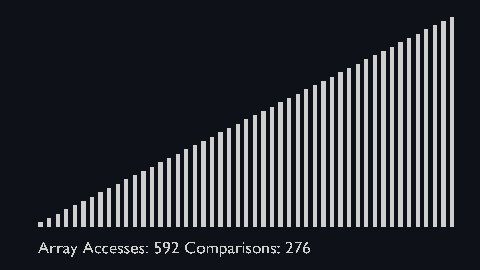|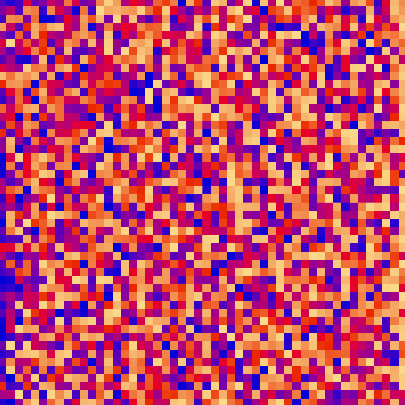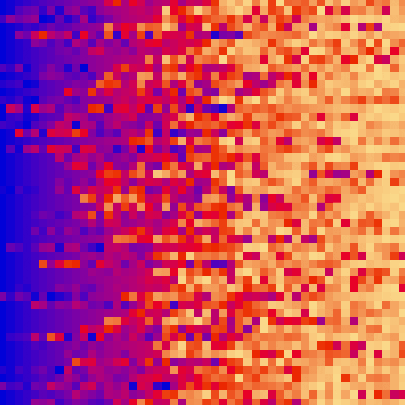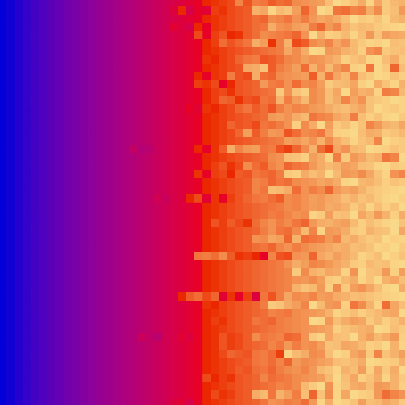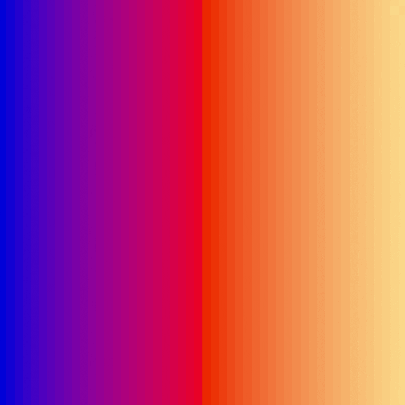||
|
||||
|
||||
Big O
|
||||
=====
|
||||
@ -348,3 +355,9 @@ However, if the value of <strong>"k"</strong> is not already known then it may b
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
### Big O Complexity Chart
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Binary file not shown.
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 28 MiB |
@ -28,10 +28,10 @@ def bubble_sort(arr, count):
|
||||
if hsv1 > hsv2:
|
||||
|
||||
#change location & insert keyframes based on bubble sort
|
||||
arr[j].rotation_euler.y = math.radians(j/2)
|
||||
arr[j].rotation_euler.y = math.radians((j+1)*2)
|
||||
arr[j].keyframe_insert(data_path="rotation_euler", frame=i+1)
|
||||
|
||||
arr[j+1].rotation_euler.y = math.radians((j-1)/2)
|
||||
arr[j+1].rotation_euler.y = math.radians(j*2)
|
||||
arr[j+1].keyframe_insert(data_path="rotation_euler", frame=i+1)
|
||||
|
||||
#rearrange arrays
|
||||
@ -175,34 +175,36 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
|
||||
#creating count * count planes with location.x = j * 2 and location.z = i * 2
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_cube_add(location=(0, 0, 0), rotation=(0, 0, 0), scale=(1, 1, 1))
|
||||
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_cube_add(location=(0, -i/count, 0), rotation=(0, 0, 0), scale=(1, 1, 1))
|
||||
|
||||
#adding all planes to an array
|
||||
i=0
|
||||
for ob in bpy.data.objects:
|
||||
planes[i]= ob
|
||||
origin_to_bottom(ob)
|
||||
ob.scale = (0.04525, 0.1, 5)
|
||||
ob.rotation_euler = (0, math.radians(i/2), 0)
|
||||
ob.scale = (0.04525, 0.1, 1.25)
|
||||
ob.rotation_euler = (0, math.radians(i*2), 0)
|
||||
i+=1
|
||||
|
||||
print(planes)
|
||||
|
||||
#sorts list of all objects based primary on their location.x and secondary on their location.z
|
||||
planes.sort(key = lambda obj: obj.rotation_euler.z)
|
||||
|
||||
#adding materials to array and set colorgradient
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
material = bpy.data.materials.new(name="")
|
||||
material.diffuse_color = (colors_r[i], colors_g[i], colors_b[i], 255)
|
||||
materials[i] = material
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
random.shuffle(index)
|
||||
#add materials to planes and planes to 2d array
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
#randomize distribution of colors for every row
|
||||
random.shuffle(materials)
|
||||
planes[i].rotation_euler.y = math.radians(index[i]*2)
|
||||
planes[i].data.materials.append(materials[i]) #add the material to the object
|
||||
|
||||
#sorts list of all objects based primary on their location.x and secondary on their location.z
|
||||
planes.sort(key = lambda obj: obj.rotation_euler.y)
|
||||
|
||||
#add cone to cover up overlapping center planes
|
||||
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_cone_add(location=(0, -1, -1), rotation=(math.radians(-90),0,0), scale =(2,2,1))
|
||||
|
||||
return(planes, count)
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
@ -210,9 +212,6 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
#setup_array(number of planes)
|
||||
planes, count = setup_array(720)#only 720 is valid
|
||||
|
||||
#sorting every subarray with bubble_sort + visualisation
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
bubble_sort(planes, count)
|
||||
planes, count = setup_array(180)
|
||||
|
||||
bubble_sort(planes, count)
|
||||
265
sort_circle/heap_sort_circle.py
Normal file
265
sort_circle/heap_sort_circle.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,265 @@
|
||||
import bpy
|
||||
import random
|
||||
import math
|
||||
from array import *
|
||||
from math import pi
|
||||
from mathutils import Vector, Matrix
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import colorsys
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Heap Sort Algorithm
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def heapify(arr, n, i):
|
||||
|
||||
global iframe
|
||||
|
||||
largest = i # Initialize largest as root
|
||||
l = 2 * i + 1 # left = 2*i + 1
|
||||
r = 2 * i + 2 # right = 2*i + 2
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
|
||||
hsv1 = mat_to_hsv(arr[largest])
|
||||
hsv2 = mat_to_hsv(arr[l])
|
||||
|
||||
except:
|
||||
print("l to big")
|
||||
|
||||
# See if left child of root exists and is greater than root
|
||||
if l < n and hsv1 < hsv2:
|
||||
largest = l
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
hsv1 = mat_to_hsv(arr[largest])
|
||||
hsv2 = mat_to_hsv(arr[r])
|
||||
|
||||
except:
|
||||
print("r to big")
|
||||
|
||||
# See if right child of root exists and is greater than root
|
||||
if r < n and hsv1 < hsv2:
|
||||
largest = r
|
||||
|
||||
# Change root, if needed
|
||||
if largest != i:
|
||||
arr[i], arr[largest] = arr[largest], arr[i] # swap
|
||||
|
||||
a = arr[i].rotation_euler.y
|
||||
b = arr[largest].rotation_euler.y
|
||||
|
||||
arr[i].rotation_euler.y = b
|
||||
arr[largest].rotation_euler.y = a
|
||||
|
||||
for cube in planes:
|
||||
cube.keyframe_insert(data_path="rotation_euler", frame=iframe)
|
||||
|
||||
iframe += 1
|
||||
|
||||
# Heapify the root.
|
||||
heapify(arr, n, largest)
|
||||
|
||||
# The main function to sort an array of given size
|
||||
def heap_sort(arr):
|
||||
|
||||
n = len(arr)
|
||||
|
||||
global iframe
|
||||
|
||||
# Build a maxheap.
|
||||
for i in range(n//2 - 1, -1, -1):
|
||||
heapify(arr, n, i)
|
||||
|
||||
# One by one extract elements
|
||||
for i in range(n-1, 0, -1):
|
||||
arr[i], arr[0] = arr[0], arr[i] # swap
|
||||
|
||||
a = arr[i].rotation_euler.y
|
||||
b = arr[0].rotation_euler.y
|
||||
|
||||
arr[i].rotation_euler.y = b
|
||||
arr[0].rotation_euler.y = a
|
||||
|
||||
for cube in planes:
|
||||
cube.keyframe_insert(data_path="rotation_euler", frame=iframe)
|
||||
|
||||
iframe += 1
|
||||
|
||||
heapify(arr, i, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
# Convert RGB to single HSV from Material
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def mat_to_hsv(ob):
|
||||
|
||||
#get materials
|
||||
mat = ob.active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
|
||||
#get R value
|
||||
r = mat[0]
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value
|
||||
g = mat[1]
|
||||
|
||||
#get b value
|
||||
b = mat[2]
|
||||
|
||||
hsv = colorsys.rgb_to_hsv(r, g, b)
|
||||
|
||||
return hsv
|
||||
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
# #Set origin of cube to bottom of mesh
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def origin_to_bottom(ob, matrix=Matrix()):
|
||||
me = ob.data
|
||||
mw = ob.matrix_world
|
||||
local_verts = [matrix @ Vector(v[:]) for v in ob.bound_box]
|
||||
o = sum(local_verts, Vector()) / 8
|
||||
o.z = min(v.z for v in local_verts)
|
||||
o = matrix.inverted() @ o
|
||||
me.transform(Matrix.Translation(-o))
|
||||
mw.translation = mw @ o
|
||||
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
# Setup Random Colors + Array of Cubes to be sorted
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def setup_array(count):
|
||||
|
||||
#set optimal color managment setting
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.exposure = -3.75
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.gamma = 0.5
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.look = 'Medium Contrast'
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.view_transform = 'Standard'
|
||||
|
||||
#fill array with numbers between 0 & count - 1
|
||||
index = list(range(count))
|
||||
|
||||
#initialize plane array
|
||||
planes = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
|
||||
#initialize material array
|
||||
materials = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
|
||||
#create all r values for hsv circle
|
||||
colors_r = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_r1 = np.linspace(0, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_r2 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_r3 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_r4 = np.linspace(255, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_r5 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_r6 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//6):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r1[i]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 2):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r2[i-count//6]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 3):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r3[i-count//6 * 2]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 4):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r4[i-count//6 * 3]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 5):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r5[i-count//6 * 4]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 6):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r6[i-count//6 * 5]
|
||||
|
||||
#create all g values for hsv circle
|
||||
colors_g = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_g1 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_g2 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_g3 = np.linspace(0, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_g4 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_g5 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_g6 = np.linspace(255, 0, count//6)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//6):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g1[i]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 2):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g2[i-count//6]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 3):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g3[i-count//6 * 2]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 4):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g4[i-count//6 * 3]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 5):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g5[i-count//6 * 4]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 6):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g6[i-count//6 * 5]
|
||||
|
||||
#create all b values for hsv circle
|
||||
colors_b = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_b1 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_b2 = np.linspace(255, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_b3 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_b4 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_b5 = np.linspace(0, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_b6 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//6):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b1[i]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 2):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b2[i-count//6]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 3):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b3[i-count//6 * 2]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 4):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b4[i-count//6 * 3]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 5):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b5[i-count//6 * 4]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 6):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b6[i-count//6 * 5]
|
||||
|
||||
#delete every existing object
|
||||
for ob in bpy.data.objects:
|
||||
bpy.data.objects.remove(ob)
|
||||
|
||||
#delete all existing materials
|
||||
for material in bpy.data.materials:
|
||||
bpy.data.materials.remove(material, do_unlink=True)
|
||||
|
||||
#creating count * count planes with location.x = j * 2 and location.z = i * 2
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_cube_add(location=(0, -i/count, 0), rotation=(0, 0, 0), scale=(1, 1, 1))
|
||||
|
||||
#adding all planes to an array
|
||||
i=0
|
||||
for ob in bpy.data.objects:
|
||||
planes[i]= ob
|
||||
origin_to_bottom(ob)
|
||||
ob.scale = (0.04525, 0.1, 1.25)
|
||||
ob.rotation_euler = (0, math.radians(i*2), 0)
|
||||
i+=1
|
||||
|
||||
#adding materials to array and set colorgradient
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
material = bpy.data.materials.new(name="")
|
||||
material.diffuse_color = (colors_r[i], colors_g[i], colors_b[i], 255)
|
||||
materials[i] = material
|
||||
|
||||
random.shuffle(index)
|
||||
#add materials to planes and planes to 2d array
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
#randomize distribution of colors for every row
|
||||
planes[i].rotation_euler.y = math.radians(index[i]*2)
|
||||
planes[i].data.materials.append(materials[i]) #add the material to the object
|
||||
|
||||
#sorts list of all objects based primary on their location.x and secondary on their location.z
|
||||
planes.sort(key = lambda obj: obj.rotation_euler.y)
|
||||
|
||||
#add cone to cover up overlapping center planes
|
||||
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_cone_add(location=(0, -1, -1), rotation=(math.radians(-90),0,0), scale =(2,2,1))
|
||||
|
||||
return(planes, count)
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Call Functions
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
#setup_array(number of planes)
|
||||
planes, count = setup_array(180)
|
||||
|
||||
iframe= 0
|
||||
heap_sort(planes)
|
||||
290
sort_circle/merge_sort_circle.py
Normal file
290
sort_circle/merge_sort_circle.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,290 @@
|
||||
import bpy
|
||||
import random
|
||||
import math
|
||||
from array import *
|
||||
from math import pi
|
||||
from mathutils import Vector, Matrix
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import colorsys
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Merge Sort Algorithm
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def merge(arr, l, m, r):
|
||||
|
||||
global planes
|
||||
global iframe
|
||||
|
||||
n1 = m - l + 1
|
||||
n2 = r - m
|
||||
|
||||
#create temp arrays
|
||||
L = [0] * (n1)
|
||||
R = [0] * (n2)
|
||||
|
||||
#copy data to temp arrays L[] and R[]
|
||||
for i in range(0, n1):
|
||||
|
||||
L[i] = arr[l + i]
|
||||
|
||||
for j in range(0, n2):
|
||||
|
||||
R[j] = arr[m + 1 + j]
|
||||
|
||||
#merge the temp arrays back into arr[l..r]
|
||||
i = 0 #initial index of first subarray
|
||||
j = 0 #initial index of second subarray
|
||||
k = l #initial index of merged subarray
|
||||
|
||||
while i < n1 and j < n2:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
hsv1 = mat_to_hsv(L[i])
|
||||
hsv2 = mat_to_hsv(R[j])
|
||||
|
||||
if hsv1 <= hsv2:
|
||||
arr[k] = L[i]
|
||||
|
||||
L[i].rotation_euler.y = math.radians(k * 2)
|
||||
|
||||
i += 1
|
||||
else:
|
||||
arr[k] = R[j]
|
||||
|
||||
R[j].rotation_euler.y = math.radians(k * 2)
|
||||
|
||||
j += 1
|
||||
k += 1
|
||||
|
||||
for cube in planes:
|
||||
cube.keyframe_insert(data_path="rotation_euler", frame=iframe)
|
||||
for cube in L:
|
||||
cube.keyframe_insert(data_path="rotation_euler", frame=iframe)
|
||||
for cube in R:
|
||||
cube.keyframe_insert(data_path="rotation_euler", frame=iframe)
|
||||
|
||||
iframe += 1
|
||||
|
||||
#copy the remaining elements of L[], if there are any
|
||||
while i < n1:
|
||||
arr[k] = L[i]
|
||||
|
||||
L[i].rotation_euler.y = math.radians(k * 2)
|
||||
|
||||
x=0
|
||||
for cube in planes:
|
||||
cube.keyframe_insert(data_path="rotation_euler", frame=iframe)
|
||||
for cube in L:
|
||||
cube.keyframe_insert(data_path="rotation_euler", frame=iframe)
|
||||
for cube in R:
|
||||
cube.keyframe_insert(data_path="rotation_euler", frame=iframe)
|
||||
iframe += 1
|
||||
|
||||
i += 1
|
||||
k += 1
|
||||
|
||||
#copy the remaining elements of R[], if there are any
|
||||
while j < n2:
|
||||
arr[k] = R[j]
|
||||
|
||||
R[j].rotation_euler.y = math.radians(k * 2)
|
||||
|
||||
for cube in planes:
|
||||
cube.keyframe_insert(data_path="rotation_euler", frame=iframe)
|
||||
for cube in L:
|
||||
cube.keyframe_insert(data_path="rotation_euler", frame=iframe)
|
||||
for cube in R:
|
||||
cube.keyframe_insert(data_path="rotation_euler", frame=iframe)
|
||||
iframe+=1
|
||||
|
||||
j += 1
|
||||
k += 1
|
||||
|
||||
#l is for left index and r is right index of the sub-array of arr to be sorted
|
||||
def merge_sort(arr, l, r):
|
||||
if l < r:
|
||||
|
||||
#same as (l+r)//2, but avoids overflow for large l and h
|
||||
m = l+(r-l)//2
|
||||
|
||||
#sort first and second halves
|
||||
merge_sort(arr, l, m)
|
||||
merge_sort(arr, m+1, r)
|
||||
merge(arr, l, m, r)
|
||||
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
# Convert RGB to single HSV from Material
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def mat_to_hsv(ob):
|
||||
|
||||
#get materials
|
||||
mat = ob.active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
|
||||
#get R value
|
||||
r = mat[0]
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value
|
||||
g = mat[1]
|
||||
|
||||
#get b value
|
||||
b = mat[2]
|
||||
|
||||
hsv = colorsys.rgb_to_hsv(r, g, b)
|
||||
|
||||
return hsv
|
||||
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
# #Set origin of cube to bottom of mesh
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def origin_to_bottom(ob, matrix=Matrix()):
|
||||
me = ob.data
|
||||
mw = ob.matrix_world
|
||||
local_verts = [matrix @ Vector(v[:]) for v in ob.bound_box]
|
||||
o = sum(local_verts, Vector()) / 8
|
||||
o.z = min(v.z for v in local_verts)
|
||||
o = matrix.inverted() @ o
|
||||
me.transform(Matrix.Translation(-o))
|
||||
mw.translation = mw @ o
|
||||
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
# Setup Random Colors + Array of Cubes to be sorted
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def setup_array(count):
|
||||
|
||||
#set optimal color managment setting
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.exposure = -3.75
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.gamma = 0.5
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.look = 'Medium Contrast'
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.view_transform = 'Standard'
|
||||
|
||||
#fill array with numbers between 0 & count - 1
|
||||
index = list(range(count))
|
||||
|
||||
#initialize plane array
|
||||
planes = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
|
||||
#initialize material array
|
||||
materials = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
|
||||
#create all r values for hsv circle
|
||||
colors_r = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_r1 = np.linspace(0, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_r2 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_r3 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_r4 = np.linspace(255, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_r5 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_r6 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//6):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r1[i]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 2):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r2[i-count//6]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 3):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r3[i-count//6 * 2]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 4):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r4[i-count//6 * 3]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 5):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r5[i-count//6 * 4]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 6):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r6[i-count//6 * 5]
|
||||
|
||||
#create all g values for hsv circle
|
||||
colors_g = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_g1 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_g2 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_g3 = np.linspace(0, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_g4 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_g5 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_g6 = np.linspace(255, 0, count//6)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//6):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g1[i]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 2):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g2[i-count//6]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 3):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g3[i-count//6 * 2]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 4):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g4[i-count//6 * 3]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 5):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g5[i-count//6 * 4]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 6):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g6[i-count//6 * 5]
|
||||
|
||||
#create all b values for hsv circle
|
||||
colors_b = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_b1 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_b2 = np.linspace(255, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_b3 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_b4 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_b5 = np.linspace(0, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_b6 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//6):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b1[i]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 2):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b2[i-count//6]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 3):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b3[i-count//6 * 2]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 4):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b4[i-count//6 * 3]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 5):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b5[i-count//6 * 4]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 6):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b6[i-count//6 * 5]
|
||||
|
||||
#delete every existing object
|
||||
for ob in bpy.data.objects:
|
||||
bpy.data.objects.remove(ob)
|
||||
|
||||
#delete all existing materials
|
||||
for material in bpy.data.materials:
|
||||
bpy.data.materials.remove(material, do_unlink=True)
|
||||
|
||||
#creating count * count planes with location.x = j * 2 and location.z = i * 2
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_cube_add(location=(0, -i/count, 0), rotation=(0, 0, 0), scale=(1, 1, 1))
|
||||
|
||||
#adding all planes to an array
|
||||
i=0
|
||||
for ob in bpy.data.objects:
|
||||
planes[i]= ob
|
||||
origin_to_bottom(ob)
|
||||
ob.scale = (0.04525, 0.1, 1.25)
|
||||
ob.rotation_euler = (0, math.radians(i*2), 0)
|
||||
i+=1
|
||||
|
||||
#adding materials to array and set colorgradient
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
material = bpy.data.materials.new(name="")
|
||||
material.diffuse_color = (colors_r[i], colors_g[i], colors_b[i], 255)
|
||||
materials[i] = material
|
||||
|
||||
random.shuffle(index)
|
||||
#add materials to planes and planes to 2d array
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
#randomize distribution of colors for every row
|
||||
planes[i].rotation_euler.y = math.radians(index[i]*2)
|
||||
planes[i].data.materials.append(materials[i]) #add the material to the object
|
||||
|
||||
#sorts list of all objects based primary on their location.x and secondary on their location.z
|
||||
planes.sort(key = lambda obj: obj.rotation_euler.y)
|
||||
|
||||
#add cone to cover up overlapping center planes
|
||||
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_cone_add(location=(0, -1, -1), rotation=(math.radians(-90),0,0), scale =(2,2,1))
|
||||
|
||||
return(planes, count)
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Call Functions
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
#setup_array(number of planes)
|
||||
planes, count = setup_array(180)
|
||||
|
||||
iframe = 0
|
||||
merge_sort(planes, 0, len(planes)-1)
|
||||
249
sort_circle/quick_sort_circle.py
Normal file
249
sort_circle/quick_sort_circle.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,249 @@
|
||||
import bpy
|
||||
import random
|
||||
import math
|
||||
from array import *
|
||||
from math import pi
|
||||
from mathutils import Vector, Matrix
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import colorsys
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Quick Sort Algorithm
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
# function to find the partition position
|
||||
def partition(array, low, high):
|
||||
|
||||
global iframe
|
||||
|
||||
pivot = array[(high + low) // 2]
|
||||
|
||||
# pointer for greater element
|
||||
i = low
|
||||
j = high
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
|
||||
hsv1 = mat_to_hsv(array[i])
|
||||
hsv2 = mat_to_hsv(pivot)
|
||||
|
||||
while hsv1 < hsv2:
|
||||
i += 1
|
||||
hsv1 = mat_to_hsv(array[i])
|
||||
hsv2 = mat_to_hsv(pivot)
|
||||
|
||||
hsv3 = mat_to_hsv(array[j])
|
||||
hsv4 = mat_to_hsv(pivot)
|
||||
|
||||
while hsv3 > hsv4:
|
||||
j -= 1
|
||||
hsv3 = mat_to_hsv(array[j])
|
||||
hsv4 = mat_to_hsv(pivot)
|
||||
|
||||
if i >= j:
|
||||
return j
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
iframe += 1
|
||||
for cube in planes:
|
||||
cube.keyframe_insert(data_path="rotation_euler", frame=iframe)
|
||||
|
||||
array[i].rotation_euler.y = math.radians(j * 2)
|
||||
array[j].rotation_euler.y = math.radians(i * 2)
|
||||
|
||||
array[i].keyframe_insert(data_path="rotation_euler", frame=iframe)
|
||||
array[j].keyframe_insert(data_path="rotation_euler", frame=iframe)
|
||||
|
||||
# swapping element at i with element at j
|
||||
array[i], array[j] = array[j], array[i]
|
||||
i+=1;
|
||||
j-=1;
|
||||
|
||||
# function to perform quicksort
|
||||
def quick_sort(array, low, high):
|
||||
if low < high:
|
||||
# find pivot element such that
|
||||
# element smaller than pivot are on the left
|
||||
# element greater than pivot are on the right
|
||||
piv = partition(array, low, high)
|
||||
|
||||
# recursive call on the left of pivot
|
||||
quick_sort(array, low, piv)
|
||||
|
||||
# recursive call on the right of pivot
|
||||
quick_sort(array, piv + 1, high)
|
||||
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
# Convert RGB to single HSV from Material
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def mat_to_hsv(ob):
|
||||
|
||||
#get materials
|
||||
mat = ob.active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
|
||||
#get R value
|
||||
r = mat[0]
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value
|
||||
g = mat[1]
|
||||
|
||||
#get b value
|
||||
b = mat[2]
|
||||
|
||||
hsv = colorsys.rgb_to_hsv(r, g, b)
|
||||
|
||||
return hsv
|
||||
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
# #Set origin of cube to bottom of mesh
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def origin_to_bottom(ob, matrix=Matrix()):
|
||||
me = ob.data
|
||||
mw = ob.matrix_world
|
||||
local_verts = [matrix @ Vector(v[:]) for v in ob.bound_box]
|
||||
o = sum(local_verts, Vector()) / 8
|
||||
o.z = min(v.z for v in local_verts)
|
||||
o = matrix.inverted() @ o
|
||||
me.transform(Matrix.Translation(-o))
|
||||
mw.translation = mw @ o
|
||||
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
# Setup Random Colors + Array of Cubes to be sorted
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def setup_array(count):
|
||||
|
||||
#set optimal color managment setting
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.exposure = -3.75
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.gamma = 0.5
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.look = 'Medium Contrast'
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.view_transform = 'Standard'
|
||||
|
||||
#fill array with numbers between 0 & count - 1
|
||||
index = list(range(count))
|
||||
|
||||
#initialize plane array
|
||||
planes = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
|
||||
#initialize material array
|
||||
materials = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
|
||||
#create all r values for hsv circle
|
||||
colors_r = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_r1 = np.linspace(0, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_r2 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_r3 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_r4 = np.linspace(255, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_r5 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_r6 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//6):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r1[i]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 2):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r2[i-count//6]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 3):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r3[i-count//6 * 2]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 4):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r4[i-count//6 * 3]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 5):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r5[i-count//6 * 4]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 6):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r6[i-count//6 * 5]
|
||||
|
||||
#create all g values for hsv circle
|
||||
colors_g = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_g1 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_g2 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_g3 = np.linspace(0, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_g4 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_g5 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_g6 = np.linspace(255, 0, count//6)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//6):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g1[i]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 2):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g2[i-count//6]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 3):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g3[i-count//6 * 2]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 4):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g4[i-count//6 * 3]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 5):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g5[i-count//6 * 4]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 6):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g6[i-count//6 * 5]
|
||||
|
||||
#create all b values for hsv circle
|
||||
colors_b = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_b1 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_b2 = np.linspace(255, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_b3 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_b4 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_b5 = np.linspace(0, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_b6 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//6):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b1[i]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 2):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b2[i-count//6]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 3):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b3[i-count//6 * 2]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 4):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b4[i-count//6 * 3]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 5):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b5[i-count//6 * 4]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 6):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b6[i-count//6 * 5]
|
||||
|
||||
#delete every existing object
|
||||
for ob in bpy.data.objects:
|
||||
bpy.data.objects.remove(ob)
|
||||
|
||||
#delete all existing materials
|
||||
for material in bpy.data.materials:
|
||||
bpy.data.materials.remove(material, do_unlink=True)
|
||||
|
||||
#creating count * count planes with location.x = j * 2 and location.z = i * 2
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_cube_add(location=(0, -i/count, 0), rotation=(0, 0, 0), scale=(1, 1, 1))
|
||||
|
||||
#adding all planes to an array
|
||||
i=0
|
||||
for ob in bpy.data.objects:
|
||||
planes[i]= ob
|
||||
origin_to_bottom(ob)
|
||||
ob.scale = (0.04525, 0.1, 1.25)
|
||||
ob.rotation_euler = (0, math.radians(i*2), 0)
|
||||
i+=1
|
||||
|
||||
#adding materials to array and set colorgradient
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
material = bpy.data.materials.new(name="")
|
||||
material.diffuse_color = (colors_r[i], colors_g[i], colors_b[i], 255)
|
||||
materials[i] = material
|
||||
|
||||
random.shuffle(index)
|
||||
#add materials to planes and planes to 2d array
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
#randomize distribution of colors for every row
|
||||
planes[i].rotation_euler.y = math.radians(index[i]*2)
|
||||
planes[i].data.materials.append(materials[i]) #add the material to the object
|
||||
|
||||
#sorts list of all objects based primary on their location.x and secondary on their location.z
|
||||
planes.sort(key = lambda obj: obj.rotation_euler.y)
|
||||
|
||||
#add cone to cover up overlapping center planes
|
||||
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_cone_add(location=(0, -1, -1), rotation=(math.radians(-90),0,0), scale =(2,2,1))
|
||||
|
||||
return(planes, count)
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Call Functions
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
#setup_array(number of planes)
|
||||
planes, count = setup_array(180)
|
||||
|
||||
iframe = 0
|
||||
quick_sort(planes, 0, count - 1)
|
||||
214
sort_circle/selection_sort_circle.py
Normal file
214
sort_circle/selection_sort_circle.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,214 @@
|
||||
import bpy
|
||||
import random
|
||||
import math
|
||||
from array import *
|
||||
from math import pi
|
||||
from mathutils import Vector, Matrix
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import colorsys
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Selection Sort Algorithm
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def selection_sort(cubes):
|
||||
|
||||
iframe = 0
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(0, len(cubes)):
|
||||
min_idx = i
|
||||
|
||||
for cube in cubes:
|
||||
cube.keyframe_insert(data_path="rotation_euler", frame= iframe)
|
||||
|
||||
for j in range(i , len(cubes)):
|
||||
|
||||
hsv1 = mat_to_hsv(cubes[min_idx])
|
||||
hsv2 = mat_to_hsv(cubes[j])
|
||||
|
||||
if hsv1 > hsv2:
|
||||
min_idx = j
|
||||
|
||||
cubes[i].rotation_euler.y = math.radians(min_idx*2)
|
||||
cubes[min_idx].rotation_euler.y = math.radians(i*2)
|
||||
|
||||
cubes[i].keyframe_insert(data_path="rotation_euler", frame= iframe)
|
||||
cubes[min_idx].keyframe_insert(data_path="rotation_euler", frame= iframe)
|
||||
iframe +=1
|
||||
|
||||
cubes[i], cubes[min_idx] = cubes[min_idx], cubes[i]
|
||||
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
# Convert RGB to single HSV from Material
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def mat_to_hsv(ob):
|
||||
|
||||
#get materials
|
||||
mat = ob.active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
|
||||
#get R value
|
||||
r = mat[0]
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value
|
||||
g = mat[1]
|
||||
|
||||
#get b value
|
||||
b = mat[2]
|
||||
|
||||
hsv = colorsys.rgb_to_hsv(r, g, b)
|
||||
|
||||
return hsv
|
||||
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
# #Set origin of cube to bottom of mesh
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def origin_to_bottom(ob, matrix=Matrix()):
|
||||
me = ob.data
|
||||
mw = ob.matrix_world
|
||||
local_verts = [matrix @ Vector(v[:]) for v in ob.bound_box]
|
||||
o = sum(local_verts, Vector()) / 8
|
||||
o.z = min(v.z for v in local_verts)
|
||||
o = matrix.inverted() @ o
|
||||
me.transform(Matrix.Translation(-o))
|
||||
mw.translation = mw @ o
|
||||
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
# Setup Random Colors + Array of Cubes to be sorted
|
||||
###########################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def setup_array(count):
|
||||
|
||||
#set optimal color managment setting
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.exposure = -3.75
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.gamma = 0.5
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.look = 'Medium Contrast'
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.view_transform = 'Standard'
|
||||
|
||||
#fill array with numbers between 0 & count - 1
|
||||
index = list(range(count))
|
||||
|
||||
#initialize plane array
|
||||
planes = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
|
||||
#initialize material array
|
||||
materials = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
|
||||
#create all r values for hsv circle
|
||||
colors_r = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_r1 = np.linspace(0, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_r2 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_r3 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_r4 = np.linspace(255, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_r5 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_r6 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//6):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r1[i]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 2):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r2[i-count//6]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 3):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r3[i-count//6 * 2]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 4):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r4[i-count//6 * 3]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 5):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r5[i-count//6 * 4]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 6):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r6[i-count//6 * 5]
|
||||
|
||||
#create all g values for hsv circle
|
||||
colors_g = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_g1 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_g2 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_g3 = np.linspace(0, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_g4 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_g5 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_g6 = np.linspace(255, 0, count//6)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//6):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g1[i]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 2):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g2[i-count//6]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 3):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g3[i-count//6 * 2]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 4):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g4[i-count//6 * 3]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 5):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g5[i-count//6 * 4]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 6):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g6[i-count//6 * 5]
|
||||
|
||||
#create all b values for hsv circle
|
||||
colors_b = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_b1 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_b2 = np.linspace(255, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_b3 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_b4 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//6)
|
||||
colors_b5 = np.linspace(0, 255, count//6)
|
||||
colors_b6 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//6)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//6):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b1[i]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 2):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b2[i-count//6]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 3):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b3[i-count//6 * 2]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 4):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b4[i-count//6 * 3]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 5):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b5[i-count//6 * 4]
|
||||
elif(i < count//6 * 6):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b6[i-count//6 * 5]
|
||||
|
||||
#delete every existing object
|
||||
for ob in bpy.data.objects:
|
||||
bpy.data.objects.remove(ob)
|
||||
|
||||
#delete all existing materials
|
||||
for material in bpy.data.materials:
|
||||
bpy.data.materials.remove(material, do_unlink=True)
|
||||
|
||||
#creating count * count planes with location.x = j * 2 and location.z = i * 2
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_cube_add(location=(0, -i/count, 0), rotation=(0, 0, 0), scale=(1, 1, 1))
|
||||
|
||||
#adding all planes to an array
|
||||
i=0
|
||||
for ob in bpy.data.objects:
|
||||
planes[i]= ob
|
||||
origin_to_bottom(ob)
|
||||
ob.scale = (0.04525, 0.1, 1.25)
|
||||
ob.rotation_euler = (0, math.radians(i*2), 0)
|
||||
i+=1
|
||||
|
||||
#adding materials to array and set colorgradient
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
material = bpy.data.materials.new(name="")
|
||||
material.diffuse_color = (colors_r[i], colors_g[i], colors_b[i], 255)
|
||||
materials[i] = material
|
||||
|
||||
random.shuffle(index)
|
||||
#add materials to planes and planes to 2d array
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
#randomize distribution of colors for every row
|
||||
planes[i].rotation_euler.y = math.radians(index[i]*2)
|
||||
planes[i].data.materials.append(materials[i]) #add the material to the object
|
||||
|
||||
#sorts list of all objects based primary on their location.x and secondary on their location.z
|
||||
planes.sort(key = lambda obj: obj.rotation_euler.y)
|
||||
|
||||
#add cone to cover up overlapping center planes
|
||||
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_cone_add(location=(0, -1, -1), rotation=(math.radians(-90),0,0), scale =(2,2,1))
|
||||
|
||||
return(planes, count)
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Call Functions
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
#setup_array(number of planes)
|
||||
planes, count = setup_array(180)#only 360 x n is valid
|
||||
|
||||
selection_sort(planes)
|
||||
@ -23,17 +23,7 @@ def bubble_sort(arr, count):
|
||||
mat1 = arr[j].active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
mat2 = arr[j + 1].active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
|
||||
#get R value of both materials
|
||||
r1 = mat1[0]
|
||||
r2 = mat2[0]
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value of both materials
|
||||
g1 = mat1[1]
|
||||
g2 = mat2[1]
|
||||
|
||||
# R + G = value for comparison
|
||||
rg1 = r1 + g1
|
||||
rg2 = r2 + g2
|
||||
rg1, rg2 = get_rg(mat1, mat2)
|
||||
|
||||
#compare first colorarray values
|
||||
if rg1 > rg2:
|
||||
@ -72,30 +62,30 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
|
||||
#create arrays for each color value (RGB) to generate the sunset gradient
|
||||
|
||||
#first half 0 --> 255, second half 255 --> 255
|
||||
#add red values to array
|
||||
colors_r = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_r1 = np.linspace(0, 254, count//2)
|
||||
colors_r2 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//2)
|
||||
colors_r1 = np.linspace(0, 225, count//2)
|
||||
colors_r2 = np.linspace(230, 255, count//2)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//2):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r1[i]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r2[i-count//2]
|
||||
|
||||
#first half 0 --> 0, second half 0 --> 200
|
||||
#add green values to array
|
||||
colors_g = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_g1 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//2)
|
||||
colors_g2 = np.linspace(10, 200, count//2)
|
||||
colors_g2 = np.linspace(20, 200, count//2)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//2):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g1[i]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g2[i-count//2]
|
||||
|
||||
#first half 200 --> 0, secondhalf 0 --> 100
|
||||
#add blue values to array
|
||||
colors_b = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_b1 = np.linspace(200, 0, count//2)
|
||||
colors_b2 = np.linspace(10, 100, count//2)
|
||||
colors_b1 = np.linspace(200, 20, count//2)
|
||||
colors_b2 = np.linspace(0, 100, count//2)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//2):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b1[i]
|
||||
@ -138,16 +128,41 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
for j in range(count):
|
||||
planes[j+i*count].data.materials.append(materials[j]) #add the material to the object
|
||||
Matrix[i][j] = planes[j+i*count]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#set optimal color managment setting
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.exposure = -3.75
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.gamma = 0.7
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.look = 'Medium Contrast'
|
||||
|
||||
return(Matrix, count)
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Get R and G Values from Material
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def get_rg(mat1, mat2):
|
||||
|
||||
#get R value of both materials
|
||||
r1 = mat1[0]
|
||||
r2 = mat2[0]
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value of both materials
|
||||
g1 = mat1[1]
|
||||
g2 = mat2[1]
|
||||
|
||||
# R + G = value for comparison
|
||||
rg1 = r1 + g1
|
||||
rg2 = r2 + g2
|
||||
|
||||
return rg1, rg2
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Call Functions
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
#setup_array(number of planes)
|
||||
Matrix, count = setup_array(26)#only even numbers are valid
|
||||
Matrix, count = setup_array(24)#only even numbers are valid
|
||||
|
||||
#sorting every subarray with bubble_sort + visualisation
|
||||
#bubble_sort + visualisation
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
bubble_sort(Matrix[i], count)
|
||||
@ -17,53 +17,33 @@ def heapify(arr, n, i, seed):
|
||||
l = 2 * i + 1 # left = 2*i + 1
|
||||
r = 2 * i + 2 # right = 2*i + 2
|
||||
|
||||
# See if left child of root exists and is
|
||||
# greater than root
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
#get materials during loop
|
||||
mat1 = arr[largest].active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
mat2 = arr[l].active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
|
||||
#get R value of both materials
|
||||
r1 = mat1[0]
|
||||
r2 = mat2[0]
|
||||
#get RG values from materials
|
||||
rg1, rg2 = get_rg(mat1, mat2)
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value of both materials
|
||||
g1 = mat1[1]
|
||||
g2 = mat2[1]
|
||||
|
||||
# R + G = value for comparison
|
||||
rg1 = r1 + g1
|
||||
rg2 = r2 + g2
|
||||
except:
|
||||
print("l to big")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# See if left child of root exists and is greater than root
|
||||
if l < n and rg1 < rg2:
|
||||
largest = l
|
||||
|
||||
# See if right child of root exists and is
|
||||
# greater than root
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
#get materials during loop
|
||||
mat1 = arr[largest].active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
mat2 = arr[r].active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
|
||||
#get R value of both materials
|
||||
r1 = mat1[0]
|
||||
r2 = mat2[0]
|
||||
#get RG values from materials
|
||||
rg1, rg2 = get_rg(mat1, mat2)
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value of both materials
|
||||
g1 = mat1[1]
|
||||
g2 = mat2[1]
|
||||
|
||||
# R + G = value for comparison
|
||||
rg1 = r1 + g1
|
||||
rg2 = r2 + g2
|
||||
except:
|
||||
print("r to big")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# See if right child of root exists and is greater than root
|
||||
if r < n and rg1 < rg2:
|
||||
largest = r
|
||||
|
||||
@ -133,30 +113,30 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
|
||||
#create arrays for each color value (RGB) to generate the sunset gradient
|
||||
|
||||
#first half 0 --> 254, second half 255 --> 255
|
||||
#add red values to array
|
||||
colors_r = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_r1 = np.linspace(0, 254, count//2)
|
||||
colors_r2 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//2)
|
||||
colors_r1 = np.linspace(0, 225, count//2)
|
||||
colors_r2 = np.linspace(230, 255, count//2)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//2):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r1[i]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r2[i-count//2]
|
||||
|
||||
#first half 0 --> 0, second half 10 --> 200
|
||||
#add green values to array
|
||||
colors_g = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_g1 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//2)
|
||||
colors_g2 = np.linspace(10, 200, count//2)
|
||||
colors_g2 = np.linspace(20, 200, count//2)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//2):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g1[i]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g2[i-count//2]
|
||||
|
||||
#first half 200 --> 0, secondhalf 10 --> 100
|
||||
#add blue values to array
|
||||
colors_b = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_b1 = np.linspace(255, 0, count//2)
|
||||
colors_b2 = np.linspace(10, 100, count//2)
|
||||
colors_b1 = np.linspace(200, 20, count//2)
|
||||
colors_b2 = np.linspace(0, 100, count//2)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//2):
|
||||
colors_b[i]=colors_b1[i]
|
||||
@ -207,11 +187,31 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
|
||||
return(Matrix, count)
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Get R and G Values from Material
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def get_rg(mat1, mat2):
|
||||
|
||||
#get R value of both materials
|
||||
r1 = mat1[0]
|
||||
r2 = mat2[0]
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value of both materials
|
||||
g1 = mat1[1]
|
||||
g2 = mat2[1]
|
||||
|
||||
# R + G = value for comparison
|
||||
rg1 = r1 + g1
|
||||
rg2 = r2 + g2
|
||||
|
||||
return rg1, rg2
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Call Functions
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
Matrix, count = setup_array(50)
|
||||
Matrix, count = setup_array(24)
|
||||
|
||||
#quick_sort every array
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
|
||||
@ -27,17 +27,7 @@ def insertion_sort(arr, count):
|
||||
mat1 = arr[j].active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
mat2 = key_item.active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
|
||||
#get R value of both materials
|
||||
r1 = mat1[0]
|
||||
r2 = mat2[0]
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value of both materials
|
||||
g1 = mat1[1]
|
||||
g2 = mat2[1]
|
||||
|
||||
# R + G = value for comparison
|
||||
rg1 = r1 + g1
|
||||
rg2 = r2 + g2
|
||||
rg1, rg2 = get_rg(mat1, mat2)
|
||||
|
||||
while j >= 0 and rg1 > rg2:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -54,17 +44,7 @@ def insertion_sort(arr, count):
|
||||
mat1 = arr[j].active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
mat2 = key_item.active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
|
||||
#get R value of both materials
|
||||
r1 = mat1[0]
|
||||
r2 = mat2[0]
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value of both materials
|
||||
g1 = mat1[1]
|
||||
g2 = mat2[1]
|
||||
|
||||
# R + G = value for comparison
|
||||
rg1 = r1 + g1
|
||||
rg2 = r2 + g2
|
||||
rg1, rg2 = get_rg(mat1, mat2)
|
||||
|
||||
#adding keyframes to all planes whenever one position/location is shifted
|
||||
for plane in arr:
|
||||
@ -111,29 +91,29 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
|
||||
#create arrays for each color value (RGB) to generate the sunset gradient
|
||||
|
||||
#first half 0 --> 255, second half 255 --> 255
|
||||
#add red values to array
|
||||
colors_r = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_r1 = np.linspace(0, 255, count//2)
|
||||
colors_r2 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//2)
|
||||
colors_r1 = np.linspace(0, 225, count//2)
|
||||
colors_r2 = np.linspace(230, 255, count//2)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//2):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r1[i]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r2[i-count//2]
|
||||
|
||||
#first half 0 --> 0, second half 0 --> 200
|
||||
#add green values to array
|
||||
colors_g = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_g1 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//2)
|
||||
colors_g2 = np.linspace(1, 200, count//2)
|
||||
colors_g2 = np.linspace(20, 200, count//2)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//2):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g1[i]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g2[i-count//2]
|
||||
|
||||
#first half 200 --> 0, secondhalf 0 --> 100
|
||||
#add blue values to array
|
||||
colors_b = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_b1 = np.linspace(200, 0, count//2)
|
||||
colors_b1 = np.linspace(200, 20, count//2)
|
||||
colors_b2 = np.linspace(0, 100, count//2)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//2):
|
||||
@ -177,14 +157,40 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
for j in range(count):
|
||||
planes[j+i*count].data.materials.append(materials[j]) #add the material to the object
|
||||
Matrix[i][j] = planes[j+i*count]
|
||||
|
||||
#set optimal color managment setting
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.exposure = -3.75
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.gamma = 0.7
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.look = 'Medium Contrast'
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return(Matrix, count)
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Get R and G Values from Material
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def get_rg(mat1, mat2):
|
||||
|
||||
#get R value of both materials
|
||||
r1 = mat1[0]
|
||||
r2 = mat2[0]
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value of both materials
|
||||
g1 = mat1[1]
|
||||
g2 = mat2[1]
|
||||
|
||||
# R + G = value for comparison
|
||||
rg1 = r1 + g1
|
||||
rg2 = r2 + g2
|
||||
|
||||
return rg1, rg2
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Call Functions
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
Matrix, count = setup_array(30)#only even numbers are valid
|
||||
Matrix, count = setup_array(24)#only even numbers are valid
|
||||
|
||||
#insertion_sort every array
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,7 +14,6 @@ def merge(seed, arr, l, m, r):
|
||||
global Matrix
|
||||
global iframe
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
n1 = m - l + 1
|
||||
n2 = r - m
|
||||
|
||||
@ -39,17 +38,8 @@ def merge(seed, arr, l, m, r):
|
||||
mat1 = L[i].active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
mat2 = R[j].active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
|
||||
#get R value of both materials
|
||||
r1 = mat1[0]
|
||||
r2 = mat2[0]
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value of both materials
|
||||
g1 = mat1[1]
|
||||
g2 = mat2[1]
|
||||
|
||||
# R + G = value for comparison
|
||||
rg1 = r1 + g1
|
||||
rg2 = r2 + g2
|
||||
#get RG values from materials
|
||||
rg1, rg2 = get_rg(mat1, mat2)
|
||||
|
||||
if rg1 <= rg2:
|
||||
arr[k] = L[i]
|
||||
@ -74,8 +64,7 @@ def merge(seed, arr, l, m, r):
|
||||
|
||||
iframe += 1
|
||||
|
||||
# Copy the remaining elements of L[], if there
|
||||
# are any
|
||||
# Copy the remaining elements of L[], if there are any
|
||||
while i < n1:
|
||||
arr[k] = L[i]
|
||||
L[i].location.x = k * 2
|
||||
@ -92,8 +81,7 @@ def merge(seed, arr, l, m, r):
|
||||
i += 1
|
||||
k += 1
|
||||
|
||||
# Copy the remaining elements of R[], if there
|
||||
# are any
|
||||
# Copy the remaining elements of R[], if there are any
|
||||
while j < n2:
|
||||
arr[k] = R[j]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -108,15 +96,14 @@ def merge(seed, arr, l, m, r):
|
||||
|
||||
j += 1
|
||||
k += 1
|
||||
# l is for left index and r is right index of the
|
||||
# sub-array of arr to be sorted
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# l is for left index and r is right index of the sub-array of arr to be sorted
|
||||
def merge_sort(seed, iframe,arr, l, r):
|
||||
if l < r:
|
||||
|
||||
# Same as (l+r)//2, but avoids overflow for
|
||||
# large l and h
|
||||
# Same as (l+r)//2, but avoids overflow for large l and h
|
||||
m = l+(r-l)//2
|
||||
|
||||
# Sort first and second halves
|
||||
merge_sort(seed, iframe,arr, l, m)
|
||||
merge_sort(seed, iframe, arr, m+1, r)
|
||||
@ -142,29 +129,29 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
|
||||
#create arrays for each color value (RGB) to generate the sunset gradient
|
||||
|
||||
#first half 0 --> 255, second half 255 --> 255
|
||||
#add red values to array
|
||||
colors_r = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_r1 = np.linspace(0, 255, count//2)
|
||||
colors_r2 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//2)
|
||||
colors_r1 = np.linspace(0, 225, count//2)
|
||||
colors_r2 = np.linspace(230, 255, count//2)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//2):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r1[i]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r2[i-count//2]
|
||||
|
||||
#first half 0 --> 0, second half 0 --> 200
|
||||
#add green values to array
|
||||
colors_g = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_g1 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//2)
|
||||
colors_g2 = np.linspace(1, 200, count//2)
|
||||
colors_g2 = np.linspace(20, 200, count//2)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//2):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g1[i]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g2[i-count//2]
|
||||
|
||||
#first half 200 --> 0, secondhalf 0 --> 100
|
||||
#add blue values to array
|
||||
colors_b = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_b1 = np.linspace(200, 0, count//2)
|
||||
colors_b1 = np.linspace(200, 20, count//2)
|
||||
colors_b2 = np.linspace(0, 100, count//2)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//2):
|
||||
@ -208,17 +195,41 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
for j in range(count):
|
||||
planes[j+i*count].data.materials.append(materials[j]) #add the material to the object
|
||||
Matrix[i][j] = planes[j+i*count]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#set optimal color managment setting
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.exposure = -3.75
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.gamma = 0.7
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.look = 'Medium Contrast'
|
||||
|
||||
return(Matrix, count)
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Get R and G Values from Material
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def get_rg(mat1, mat2):
|
||||
#get R value of both materials
|
||||
r1 = mat1[0]
|
||||
r2 = mat2[0]
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value of both materials
|
||||
g1 = mat1[1]
|
||||
g2 = mat2[1]
|
||||
|
||||
# R + G = value for comparison
|
||||
rg1 = r1 + g1
|
||||
rg2 = r2 + g2
|
||||
|
||||
return rg1, rg2
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Call Functions
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
#setup_array(number of planes)
|
||||
Matrix, count = setup_array(26)#only even numbers are valid
|
||||
Matrix, count = setup_array(24)#only even numbers are valid
|
||||
|
||||
#sorting every subarray with merge_sort + visualisation
|
||||
#merge_sort + visualisation
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
iframe = 0
|
||||
merge_sort(i,iframe,Matrix[i], 0, count-1)
|
||||
@ -25,66 +25,30 @@ def partition(seed, array, low, high):
|
||||
mat1 = array[i].active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
mat2 = pivot.active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
|
||||
#get R value of both materials
|
||||
r1 = mat1[0]
|
||||
r2 = mat2[0]
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value of both materials
|
||||
g1 = mat1[1]
|
||||
g2 = mat2[1]
|
||||
|
||||
# R + G = value for comparison
|
||||
rg1 = r1 + g1
|
||||
rg2 = r2 + g2
|
||||
#get RG values from materials
|
||||
rg1, rg2 = get_rg(mat1, mat2)
|
||||
|
||||
while rg1 < rg2:
|
||||
i += 1
|
||||
mat1 = array[i].active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
mat2 = pivot.active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
|
||||
#get R value of both materials
|
||||
r1 = mat1[0]
|
||||
r2 = mat2[0]
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value of both materials
|
||||
g1 = mat1[1]
|
||||
g2 = mat2[1]
|
||||
|
||||
# R + G = value for comparison
|
||||
rg1 = r1 + g1
|
||||
rg2 = r2 + g2
|
||||
#get RG values from materials
|
||||
rg1, rg2 = get_rg(mat1, mat2)
|
||||
|
||||
mat3 = array[j].active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
mat4 = pivot.active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
mat1 = array[j].active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
mat2 = pivot.active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
|
||||
#get R value of both materials
|
||||
r3 = mat3[0]
|
||||
r4 = mat4[0]
|
||||
#get RG values from materials
|
||||
rg1, rg2 = get_rg(mat1, mat2)
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value of both materials
|
||||
g3 = mat3[1]
|
||||
g4 = mat4[1]
|
||||
|
||||
# R + G = value for comparison
|
||||
rg3 = r3 + g3
|
||||
rg4 = r4 + g4
|
||||
|
||||
while rg3 > rg4:
|
||||
while rg1 > rg2:
|
||||
j -= 1
|
||||
mat3 = array[j].active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
mat4 = pivot.active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
mat1 = array[j].active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
mat2 = pivot.active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
|
||||
#get R value of both materials
|
||||
r3 = mat3[0]
|
||||
r4 = mat4[0]
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value of both materials
|
||||
g3 = mat3[1]
|
||||
g4 = mat4[1]
|
||||
|
||||
# R + G = value for comparison
|
||||
rg3 = r3 + g3
|
||||
rg4 = r4 + g4
|
||||
#get RG values from materials
|
||||
rg1, rg2 = get_rg(mat1, mat2)
|
||||
|
||||
if i >= j:
|
||||
return j
|
||||
@ -138,29 +102,29 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
|
||||
#create arrays for each color value (RGB) to generate the sunset gradient
|
||||
|
||||
#first half 0 --> 255, second half 255 --> 255
|
||||
#add red values to array
|
||||
colors_r = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_r1 = np.linspace(0, 255, count//2)
|
||||
colors_r2 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//2)
|
||||
colors_r1 = np.linspace(0, 225, count//2)
|
||||
colors_r2 = np.linspace(230, 255, count//2)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//2):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r1[i]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r2[i-count//2]
|
||||
|
||||
#first half 0 --> 0, second half 0 --> 200
|
||||
#add green values to array
|
||||
colors_g = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_g1 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//2)
|
||||
colors_g2 = np.linspace(1, 200, count//2)
|
||||
colors_g2 = np.linspace(20, 200, count//2)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//2):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g1[i]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g2[i-count//2]
|
||||
|
||||
#first half 200 --> 0, secondhalf 0 --> 100
|
||||
#add blue values to array
|
||||
colors_b = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_b1 = np.linspace(200, 0, count//2)
|
||||
colors_b1 = np.linspace(200, 20, count//2)
|
||||
colors_b2 = np.linspace(0, 100, count//2)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//2):
|
||||
@ -199,20 +163,45 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
|
||||
#add materials to planes and planes to 2d array
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
|
||||
#randomize distribution of colors for every row
|
||||
random.shuffle(materials)
|
||||
for j in range(count):
|
||||
planes[j+i*count].data.materials.append(materials[j]) #add the material to the object
|
||||
Matrix[i][j] = planes[j+i*count]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#set optimal color managment setting
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.exposure = -3.75
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.gamma = 0.7
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.look = 'Medium Contrast'
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.view_transform = 'Standard'
|
||||
|
||||
return(Matrix, count)
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Get R and G Values from Material
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def get_rg(mat1, mat2):
|
||||
#get R value of both materials
|
||||
r1 = mat1[0]
|
||||
r2 = mat2[0]
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value of both materials
|
||||
g1 = mat1[1]
|
||||
g2 = mat2[1]
|
||||
|
||||
# R + G = value for comparison
|
||||
rg1 = r1 + g1
|
||||
rg2 = r2 + g2
|
||||
|
||||
return rg1, rg2
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Call Functions
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
Matrix, count = setup_array(12)
|
||||
Matrix, count = setup_array(24)#only even numbers are valid
|
||||
|
||||
#quick_sort every array
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
|
||||
@ -25,17 +25,8 @@ def selection_sort(arr, count):
|
||||
mat1 = arr[min_idx].active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
mat2 = arr[j].active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
|
||||
#get R value of both materials
|
||||
r1 = mat1[0]
|
||||
r2 = mat2[0]
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value of both materials
|
||||
g1 = mat1[1]
|
||||
g2 = mat2[1]
|
||||
|
||||
# R + G = value for comparison
|
||||
rg1 = r1 + g1
|
||||
rg2 = r2 + g2
|
||||
#get RG values from materials
|
||||
rg1, rg2 = get_rg(mat1, mat2)
|
||||
|
||||
if rg1 > rg2:
|
||||
min_idx = j
|
||||
@ -69,29 +60,29 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
|
||||
#create arrays for each color value (RGB) to generate the sunset gradient
|
||||
|
||||
#first half 0 --> 255, second half 255 --> 255
|
||||
#add red values to array
|
||||
colors_r = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_r1 = np.linspace(0, 255, count//2)
|
||||
colors_r2 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//2)
|
||||
colors_r1 = np.linspace(0, 225, count//2)
|
||||
colors_r2 = np.linspace(230, 255, count//2)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//2):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r1[i]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r2[i-count//2]
|
||||
|
||||
#first half 0 --> 0, second half 0 --> 200
|
||||
#add green values to array
|
||||
colors_g = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_g1 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//2)
|
||||
colors_g2 = np.linspace(1, 200, count//2)
|
||||
colors_g2 = np.linspace(20, 200, count//2)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//2):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g1[i]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g2[i-count//2]
|
||||
|
||||
#first half 200 --> 0, secondhalf 0 --> 100
|
||||
#add blue values to array
|
||||
colors_b = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_b1 = np.linspace(200, 0, count//2)
|
||||
colors_b1 = np.linspace(200, 20, count//2)
|
||||
colors_b2 = np.linspace(0, 100, count//2)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//2):
|
||||
@ -135,16 +126,39 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
for j in range(count):
|
||||
planes[j+i*count].data.materials.append(materials[j]) #add the material to the object
|
||||
Matrix[i][j] = planes[j+i*count]
|
||||
|
||||
#set optimal color managment setting
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.exposure = -3.75
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.gamma = 0.7
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.look = 'Medium Contrast'
|
||||
|
||||
return(Matrix, count)
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Get R and G Values from Material
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def get_rg(mat1, mat2):
|
||||
#get R value of both materials
|
||||
r1 = mat1[0]
|
||||
r2 = mat2[0]
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value of both materials
|
||||
g1 = mat1[1]
|
||||
g2 = mat2[1]
|
||||
|
||||
# R + G = value for comparison
|
||||
rg1 = r1 + g1
|
||||
rg2 = r2 + g2
|
||||
|
||||
return rg1, rg2
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Call Functions
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
Matrix, count = setup_array(24)
|
||||
Matrix, count = setup_array(24)#only even numbers are valid
|
||||
|
||||
#selection_sort every array
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
selection_sort(Matrix[i], count)
|
||||
|
||||
selection_sort(Matrix[i], count)
|
||||
@ -35,17 +35,8 @@ def shell_sort(arr, count):
|
||||
mat1 = arr[i+gap].active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
mat2 = arr[i].active_material.diffuse_color
|
||||
|
||||
#get R value of both materials
|
||||
r1 = mat1[0]
|
||||
r2 = mat2[0]
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value of both materials
|
||||
g1 = mat1[1]
|
||||
g2 = mat2[1]
|
||||
|
||||
# R + G = value for comparison
|
||||
rg1 = r1 + g1
|
||||
rg2 = r2 + g2
|
||||
#get RG values from materials
|
||||
rg1, rg2 = get_rg(mat1, mat2)
|
||||
|
||||
if rg1 > rg2:
|
||||
break
|
||||
@ -85,29 +76,29 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
|
||||
#create arrays for each color value (RGB) to generate the sunset gradient
|
||||
|
||||
#first half 0 --> 255, second half 255 --> 255
|
||||
#add red values to array
|
||||
colors_r = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_r1 = np.linspace(0, 255, count//2)
|
||||
colors_r2 = np.linspace(255, 255, count//2)
|
||||
colors_r1 = np.linspace(0, 225, count//2)
|
||||
colors_r2 = np.linspace(230, 255, count//2)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//2):
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r1[i]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
colors_r[i]=colors_r2[i-count//2]
|
||||
|
||||
#first half 0 --> 0, second half 0 --> 200
|
||||
#add green values to array
|
||||
colors_g = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_g1 = np.linspace(0, 0, count//2)
|
||||
colors_g2 = np.linspace(1, 200, count//2)
|
||||
colors_g2 = np.linspace(20, 200, count//2)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//2):
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g1[i]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
colors_g[i]=colors_g2[i-count//2]
|
||||
|
||||
#first half 200 --> 0, secondhalf 0 --> 100
|
||||
#add blue values to array
|
||||
colors_b = [0 for i in range(count)]
|
||||
colors_b1 = np.linspace(200, 0, count//2)
|
||||
colors_b1 = np.linspace(200, 20, count//2)
|
||||
colors_b2 = np.linspace(0, 100, count//2)
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
if(i < count//2):
|
||||
@ -151,16 +142,39 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
for j in range(count):
|
||||
planes[j+i*count].data.materials.append(materials[j]) #add the material to the object
|
||||
Matrix[i][j] = planes[j+i*count]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#set optimal color managment setting
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.exposure = -3.75
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.gamma = 0.7
|
||||
bpy.context.scene.view_settings.look = 'Medium Contrast'
|
||||
|
||||
return(Matrix, count)
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Get R and G Values from Material
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def get_rg(mat1, mat2):
|
||||
#get R value of both materials
|
||||
r1 = mat1[0]
|
||||
r2 = mat2[0]
|
||||
|
||||
#get G value of both materials
|
||||
g1 = mat1[1]
|
||||
g2 = mat2[1]
|
||||
|
||||
# R + G = value for comparison
|
||||
rg1 = r1 + g1
|
||||
rg2 = r2 + g2
|
||||
|
||||
return rg1, rg2
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
# Call Functions
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
Matrix, count = setup_array(24)
|
||||
Matrix, count = setup_array(24)#only even numbers are valid
|
||||
|
||||
#shell_sort every array
|
||||
for i in range(count):
|
||||
shell_sort(Matrix[i], count)
|
||||
|
||||
shell_sort(Matrix[i], count)
|
||||
@ -7,33 +7,35 @@ from mathutils import Vector, Matrix
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def bubble_sort(cubes, arrayCounter, comparisonCounter):
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(len(cubes)-1):
|
||||
|
||||
#insert keyframe for every cube on every frame
|
||||
for cube in cubes:
|
||||
cube.keyframe_insert(data_path="location", frame=i)
|
||||
cube.keyframe_insert(data_path="location", frame=i+1)
|
||||
|
||||
already_sorted = True
|
||||
for j in range(len(cubes) - i -1):
|
||||
|
||||
#add 1 to comparison counter
|
||||
comparisonCounter.inputs[0].default_value += 1
|
||||
comparisonCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=i)
|
||||
comparisonCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=i+1)
|
||||
|
||||
#add 2 to array counter
|
||||
arrayCounter.inputs[0].default_value += 2
|
||||
arrayCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=i)
|
||||
arrayCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=i+1)
|
||||
|
||||
if cubes[j].scale.z > cubes[j + 1].scale.z:
|
||||
|
||||
#change location & insert keyframes based on bubble sort
|
||||
cubes[j].location.x = j
|
||||
cubes[j].keyframe_insert(data_path="location", frame=i)
|
||||
cubes[j].keyframe_insert(data_path="location", frame=i+1)
|
||||
cubes[j+1].location.x = j-1
|
||||
cubes[j+1].keyframe_insert(data_path="location", frame=i)
|
||||
cubes[j+1].keyframe_insert(data_path="location", frame=i+1)
|
||||
|
||||
#add 4 to array counter
|
||||
arrayCounter.inputs[0].default_value += 4
|
||||
arrayCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=i)
|
||||
arrayCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=i+1)
|
||||
|
||||
#rearrange arrays
|
||||
cubes[j], cubes[j + 1] = cubes[j + 1], cubes[j]
|
||||
@ -98,6 +100,10 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
node_grp.links.new(comparisonString.outputs[0], joinStrings.inputs[1])
|
||||
node_grp.links.new(arrayCounter.outputs[0], joinStrings.inputs[1])
|
||||
node_grp.links.new(arrayString.outputs[0], joinStrings.inputs[1])
|
||||
|
||||
#add keyframe on frame 0 for comparison and array counter
|
||||
comparisonCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=0)
|
||||
arrayCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=0)
|
||||
|
||||
#fill arrays with numbers between 1 & count
|
||||
ran = list(range(0,count-1))
|
||||
@ -141,6 +147,6 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
# Call Functions
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
cubes, arrayCounter, comparisonCounter = setup_array(20)
|
||||
cubes, arrayCounter, comparisonCounter = setup_array(50)
|
||||
|
||||
bubble_sort(cubes, arrayCounter, comparisonCounter)
|
||||
@ -13,48 +13,62 @@ def heapify(arr, n, i):
|
||||
largest = i # Initialize largest as root
|
||||
l = 2 * i + 1 # left = 2*i + 1
|
||||
r = 2 * i + 2 # right = 2*i + 2
|
||||
|
||||
# See if left child of root exists and is
|
||||
# greater than root
|
||||
|
||||
#add 2 to arrayCounter
|
||||
arrayCounter.inputs[0].default_value += 2
|
||||
arrayCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=iframe)
|
||||
#add 1 to comparisonCounter
|
||||
comparisonCounter.inputs[0].default_value += 2
|
||||
comparisonCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=iframe)
|
||||
# See if left child of root exists and is greater than root
|
||||
if l < n and arr[largest].scale.z - 1 < arr[l].scale.z - 1:
|
||||
largest = l
|
||||
|
||||
# See if right child of root exists and is
|
||||
# greater than root
|
||||
|
||||
#add 2 to arrayCounter
|
||||
arrayCounter.inputs[0].default_value += 2
|
||||
arrayCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=iframe)
|
||||
#add 1 to comparisonCounter
|
||||
comparisonCounter.inputs[0].default_value += 2
|
||||
comparisonCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=iframe)
|
||||
# See if right child of root exists and is greater than root
|
||||
if r < n and arr[largest].scale.z - 1 < arr[r].scale.z - 1:
|
||||
largest = r
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Change root, if needed
|
||||
if largest != i:
|
||||
arr[i], arr[largest] = arr[largest], arr[i] # swap
|
||||
arr[i], arr[largest] = arr[largest], arr[i] #swap
|
||||
|
||||
a = arr[i].location.x
|
||||
b = arr[largest].location.x
|
||||
|
||||
arr[i].location.x = b
|
||||
arr[largest].location.x = a
|
||||
|
||||
#add 4 to arrayCounter
|
||||
arrayCounter.inputs[0].default_value += 4
|
||||
arrayCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=iframe)
|
||||
|
||||
for cube in cubes:
|
||||
cube.keyframe_insert(data_path="location", frame=iframe)
|
||||
|
||||
iframe += 1
|
||||
|
||||
# Heapify the root.
|
||||
heapify(arr, n, largest)
|
||||
|
||||
# The main function to sort an array of given size
|
||||
def heap_sort(arr):
|
||||
|
||||
n = len(arr)
|
||||
|
||||
global iframe
|
||||
|
||||
n = len(arr)
|
||||
|
||||
# Build a maxheap.
|
||||
for i in range(n//2 - 1, -1, -1):
|
||||
heapify(arr, n, i)
|
||||
|
||||
# One by one extract elements
|
||||
for i in range(n-1, 0, -1):
|
||||
arr[i], arr[0] = arr[0], arr[i] # swap
|
||||
arr[i], arr[0] = arr[0], arr[i] #swap
|
||||
|
||||
a = arr[i].location.x
|
||||
b = arr[0].location.x
|
||||
@ -62,6 +76,10 @@ def heap_sort(arr):
|
||||
arr[i].location.x = b
|
||||
arr[0].location.x = a
|
||||
|
||||
#add 4 to arrayCounter
|
||||
arrayCounter.inputs[0].default_value += 4
|
||||
arrayCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=iframe)
|
||||
|
||||
for cube in cubes:
|
||||
cube.keyframe_insert(data_path="location", frame=iframe)
|
||||
iframe += 1
|
||||
@ -125,6 +143,10 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
node_grp.links.new(comparisonString.outputs[0], joinStrings.inputs[1])
|
||||
node_grp.links.new(arrayCounter.outputs[0], joinStrings.inputs[1])
|
||||
node_grp.links.new(arrayString.outputs[0], joinStrings.inputs[1])
|
||||
|
||||
#add keyframe on frame 0 for comparison and array counter
|
||||
comparisonCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=0)
|
||||
arrayCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=0)
|
||||
|
||||
#fill arrays with numbers between 1 & count
|
||||
ran = list(range(0,count-1))
|
||||
@ -172,5 +194,5 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
|
||||
cubes, arrayCounter, comparisonCounter = setup_array(50)
|
||||
|
||||
iframe = 0
|
||||
heap_sort(cubes)
|
||||
iframe = 1
|
||||
heap_sort(cubes)
|
||||
@ -7,9 +7,10 @@ from mathutils import Vector, Matrix
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
def insertion_sort(cubes, arrayCounter, comparisonCounter):
|
||||
|
||||
#start at frame 0
|
||||
iframe=0
|
||||
originFrame = 0
|
||||
iframe = 1
|
||||
originFrame = 1
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(0, len(cubes)):
|
||||
#defines key_item that is compared until correct location
|
||||
@ -126,6 +127,10 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
node_grp.links.new(comparisonString.outputs[0], joinStrings.inputs[1])
|
||||
node_grp.links.new(arrayCounter.outputs[0], joinStrings.inputs[1])
|
||||
node_grp.links.new(arrayString.outputs[0], joinStrings.inputs[1])
|
||||
|
||||
#add keyframe on frame 0 for comparison and array counter
|
||||
comparisonCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=0)
|
||||
arrayCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=0)
|
||||
|
||||
#fill arrays with numbers between 1 & count
|
||||
ran = list(range(0,count-1))
|
||||
@ -169,6 +174,6 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
# Call Functions
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
cubes, arrayCounter, comparisonCounter = setup_array(12)
|
||||
cubes, arrayCounter, comparisonCounter = setup_array(50)
|
||||
|
||||
insertion_sort(cubes, arrayCounter, comparisonCounter)
|
||||
insertion_sort(cubes, arrayCounter, comparisonCounter)
|
||||
@ -192,6 +192,10 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
node_grp.links.new(comparisonString.outputs[0], joinStrings.inputs[1])
|
||||
node_grp.links.new(arrayCounter.outputs[0], joinStrings.inputs[1])
|
||||
node_grp.links.new(arrayString.outputs[0], joinStrings.inputs[1])
|
||||
|
||||
#add keyframe on frame 0 for comparison and array counter
|
||||
comparisonCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=0)
|
||||
arrayCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=0)
|
||||
|
||||
#fill arrays with numbers between 1 & count
|
||||
ran = list(range(0,count-1))
|
||||
@ -235,7 +239,7 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
# Call Functions
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
cubes, arrayCounter, comparisonCounter = setup_array(20)
|
||||
cubes, arrayCounter, comparisonCounter = setup_array(50)
|
||||
|
||||
iframe = 0
|
||||
iframe = 1
|
||||
merge_sort(cubes, 0, len(cubes)-1, arrayCounter, comparisonCounter)
|
||||
@ -129,6 +129,10 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
node_grp.links.new(comparisonString.outputs[0], joinStrings.inputs[1])
|
||||
node_grp.links.new(arrayCounter.outputs[0], joinStrings.inputs[1])
|
||||
node_grp.links.new(arrayString.outputs[0], joinStrings.inputs[1])
|
||||
|
||||
#add keyframe on frame 0 for comparison and array counter
|
||||
comparisonCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=0)
|
||||
arrayCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=0)
|
||||
|
||||
#fill arrays with numbers between 1 & count
|
||||
ran = list(range(0,count-1))
|
||||
@ -172,7 +176,7 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
# Call Functions
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
cubes, arrayCounter, comparisonCounter = setup_array(20)
|
||||
cubes, arrayCounter, comparisonCounter = setup_array(50)
|
||||
|
||||
iframe = 0
|
||||
iframe = 1
|
||||
quick_sort(cubes, 0, len(cubes) - 1, arrayCounter, comparisonCounter)
|
||||
@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ from mathutils import Vector, Matrix
|
||||
|
||||
def selection_sort(cubes, arrayCounter, comparisonCounter):
|
||||
|
||||
global iframe
|
||||
iframe = 1
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(0, len(cubes)):
|
||||
min_idx = i
|
||||
@ -98,6 +98,10 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
node_grp.links.new(comparisonString.outputs[0], joinStrings.inputs[1])
|
||||
node_grp.links.new(arrayCounter.outputs[0], joinStrings.inputs[1])
|
||||
node_grp.links.new(arrayString.outputs[0], joinStrings.inputs[1])
|
||||
|
||||
#add keyframe on frame 0 for comparison and array counter
|
||||
comparisonCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=0)
|
||||
arrayCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=0)
|
||||
|
||||
#fill arrays with numbers between 1 & count
|
||||
ran = list(range(0,count-1))
|
||||
@ -141,7 +145,6 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
# Call Functions
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
cubes, arrayCounter, comparisonCounter = setup_array(20)
|
||||
cubes, arrayCounter, comparisonCounter = setup_array(50)
|
||||
|
||||
iframe = 0
|
||||
selection_sort(cubes, arrayCounter, comparisonCounter)
|
||||
@ -116,6 +116,10 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
node_grp.links.new(arrayCounter.outputs[0], joinStrings.inputs[1])
|
||||
node_grp.links.new(arrayString.outputs[0], joinStrings.inputs[1])
|
||||
|
||||
#add keyframe on frame 0 for comparison and array counter
|
||||
comparisonCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=0)
|
||||
arrayCounter.inputs[0].keyframe_insert(data_path='default_value', frame=0)
|
||||
|
||||
#fill arrays with numbers between 1 & count
|
||||
ran = list(range(0,count-1))
|
||||
|
||||
@ -158,7 +162,7 @@ def setup_array(count):
|
||||
# Call Functions
|
||||
############################################################
|
||||
|
||||
cubes, arrayCounter, comparisonCounter = setup_array(20)
|
||||
cubes, arrayCounter, comparisonCounter = setup_array(50)
|
||||
|
||||
iframe = 0
|
||||
iframe = 1
|
||||
shellSort(cubes, len(cubes), arrayCounter, comparisonCounter)
|
||||
Loading…
x
Reference in New Issue
Block a user