Update README.md
This commit is contained in:
parent
58731ff34a
commit
f03e305791
17
README.md
17
README.md
@ -44,7 +44,8 @@ Its name comes from the way the algorithm works: With every new pass, the larges
|
||||
|
||||
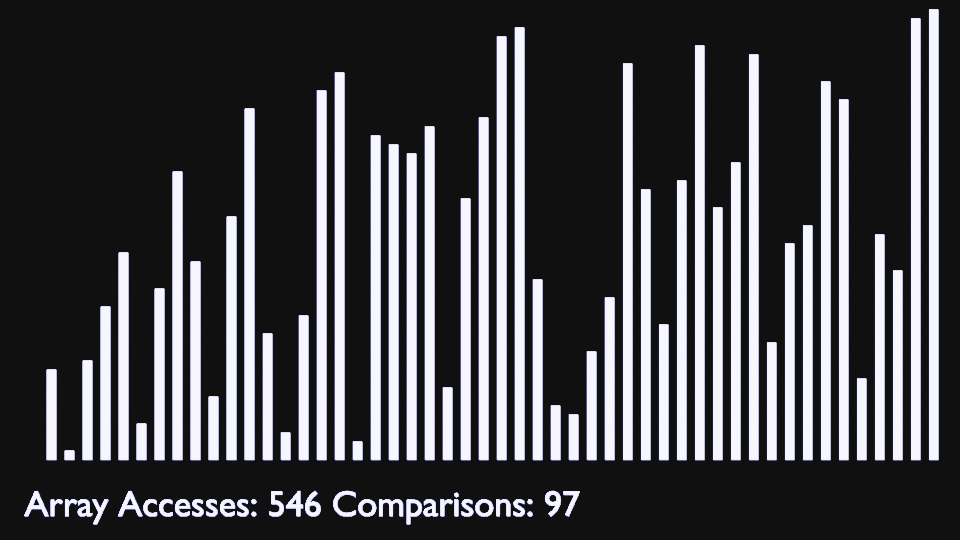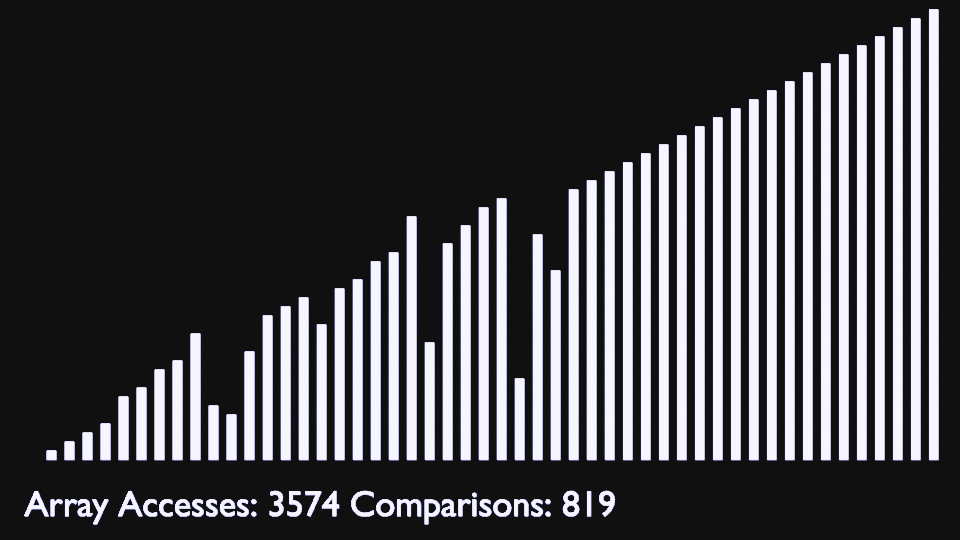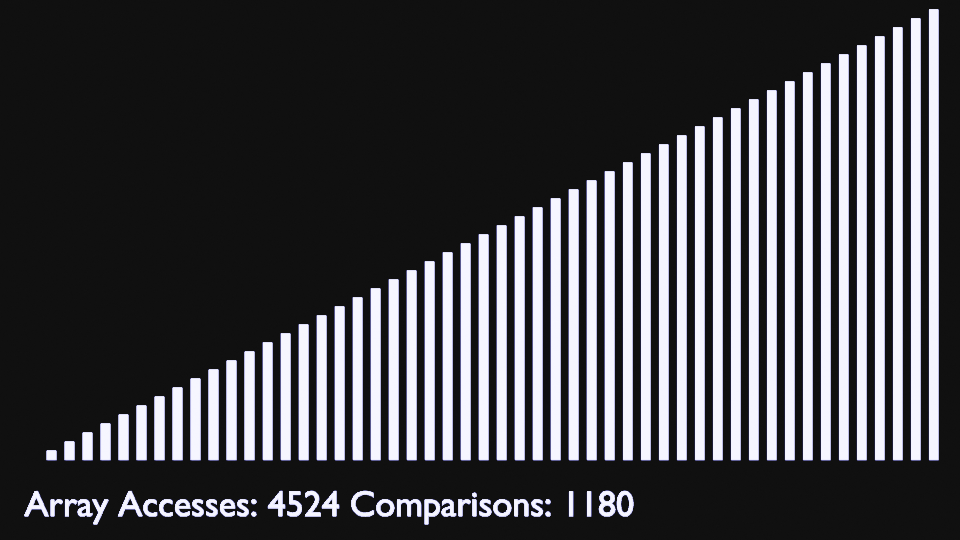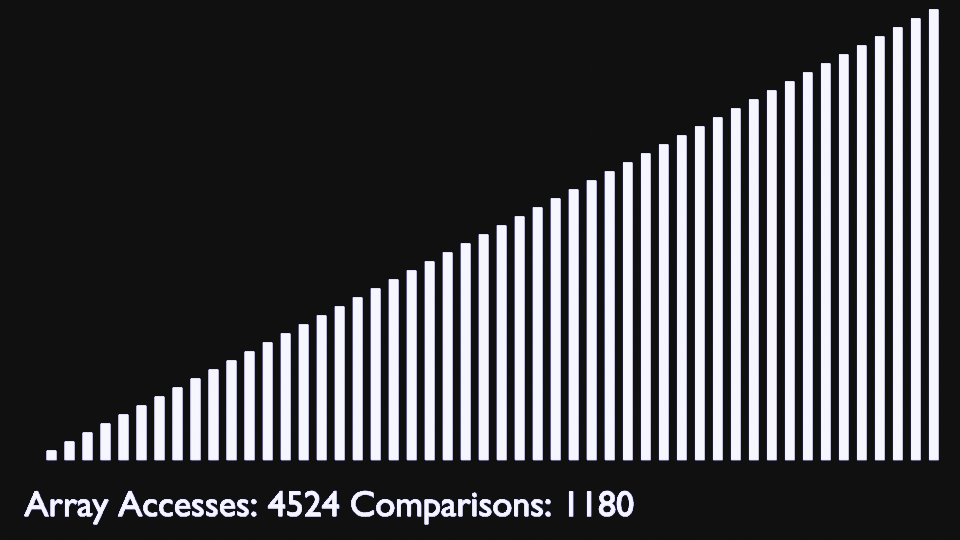
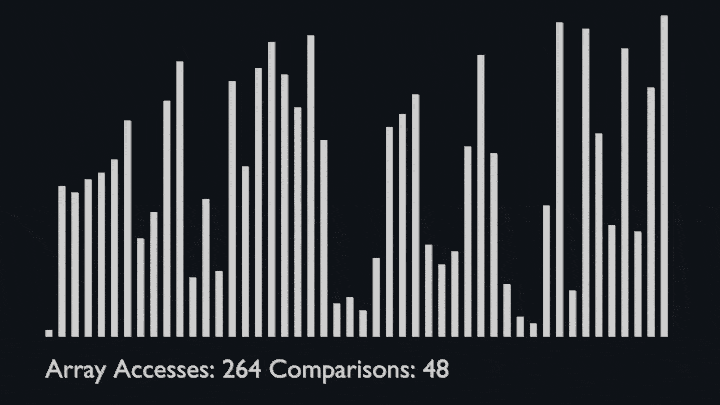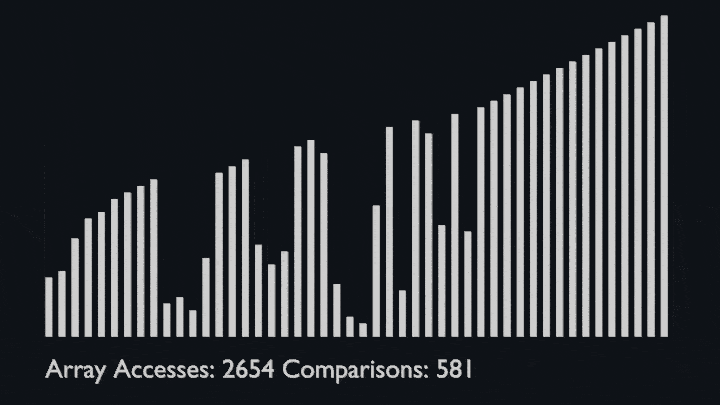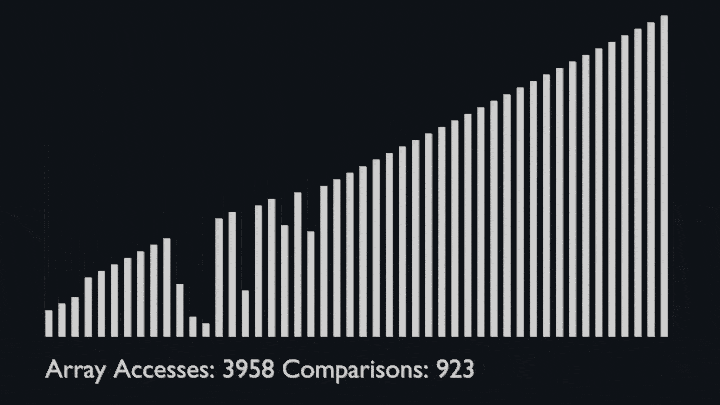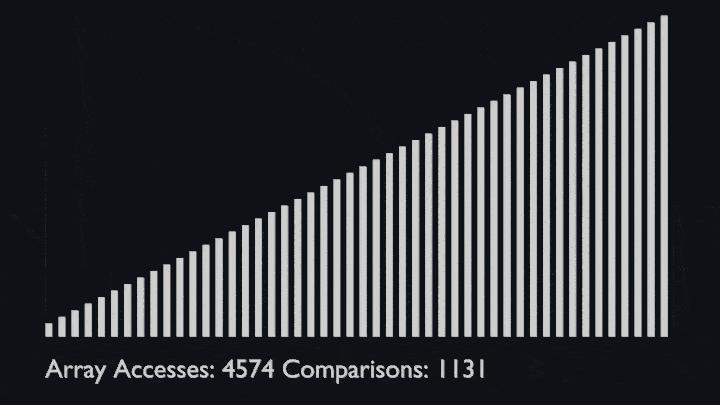
Bubble sort consists of making multiple passes through a list, comparing elements one by one, and swapping adjacent items that are out of order.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_scale/bubble_sort_scale.py" target="_blank">Script</a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Insertion Sort
|
||||
@ -52,7 +53,9 @@ Bubble sort consists of making multiple passes through a list, comparing element
|
||||
Like bubble sort, the insertion sort algorithm is straightforward to implement and understand.<br>
|
||||
But unlike bubble sort, it builds the sorted list one element at a time by comparing each item with the rest of the list and inserting it into its correct position.
|
||||
This “insertion” procedure gives the algorithm its name.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_scale/insertion_sort_scale.py" target="_blank">Script</a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Selection Sort
|
||||
@ -64,7 +67,8 @@ The selection sort algorithm sorts an array by repeatedly finding the minimum el
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
In every iteration of selection sort, the minimum element (considering ascending order) from the unsorted subarray is picked and moved to the sorted subarray.
|
||||
|
||||
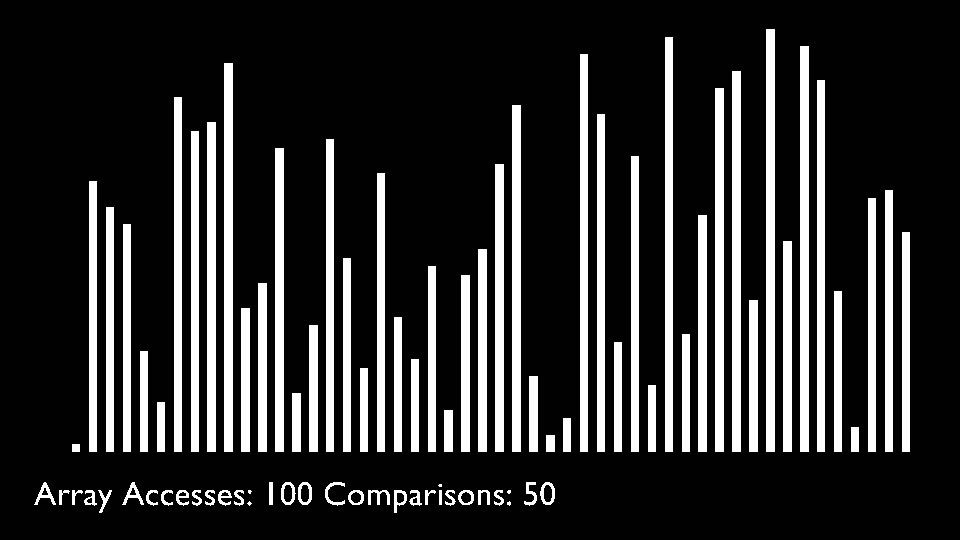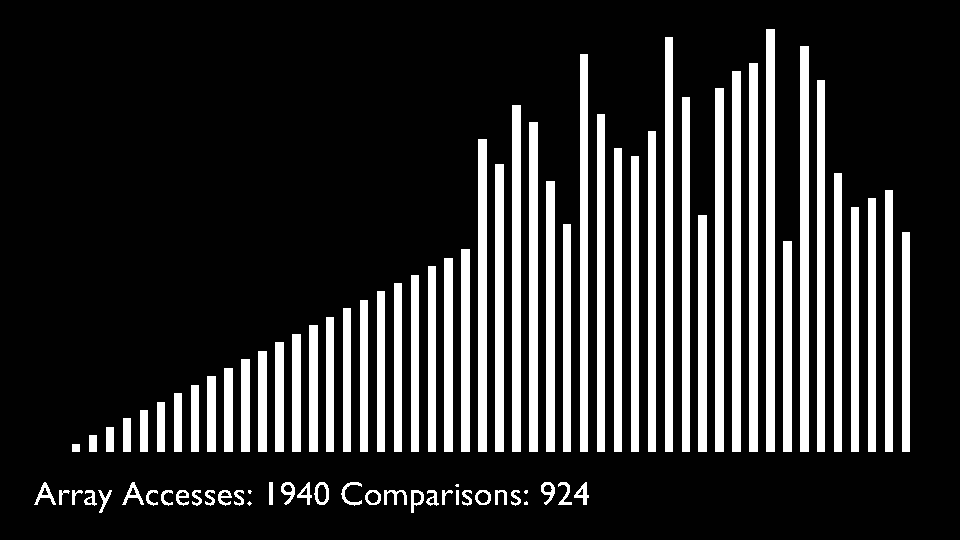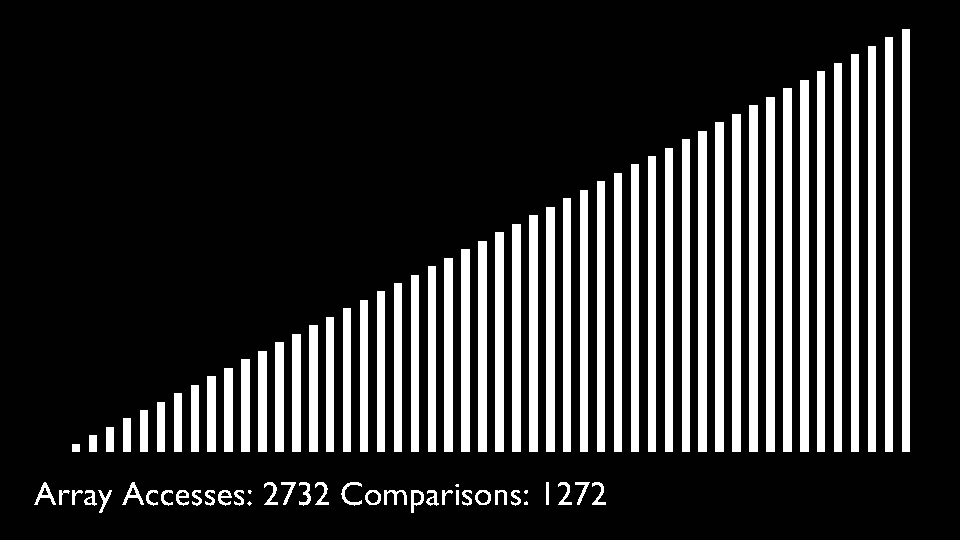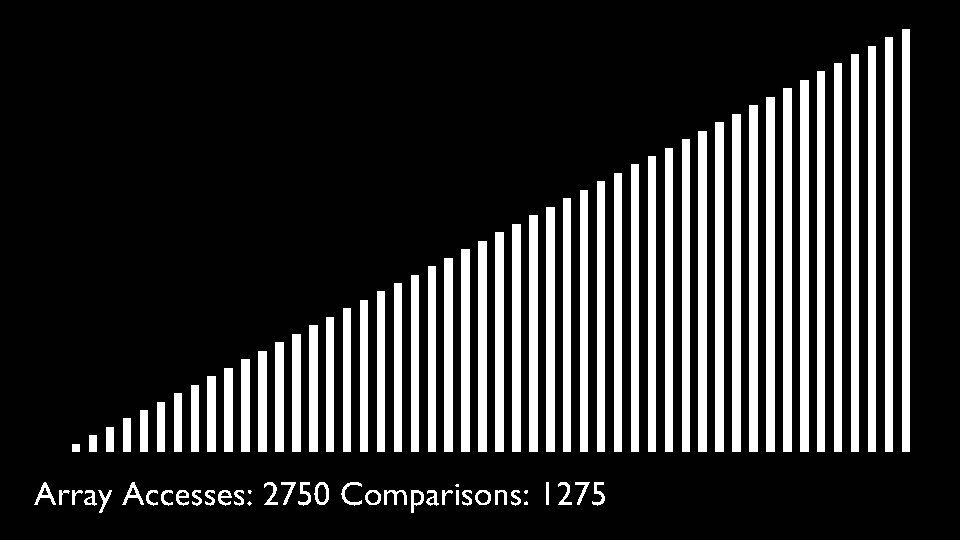
|
||||
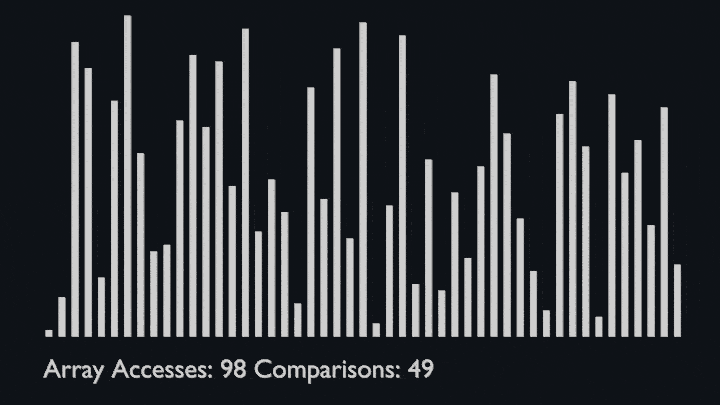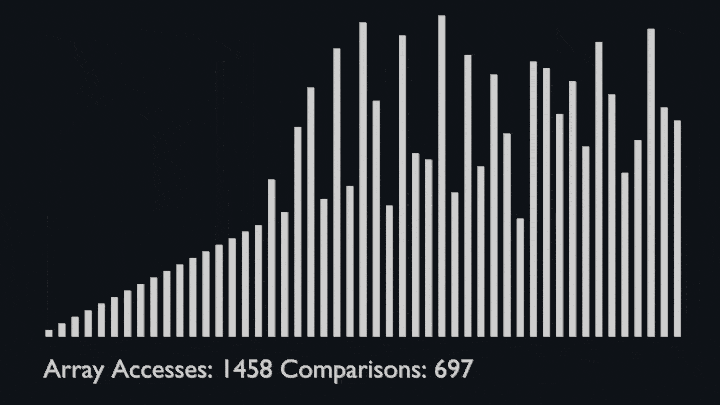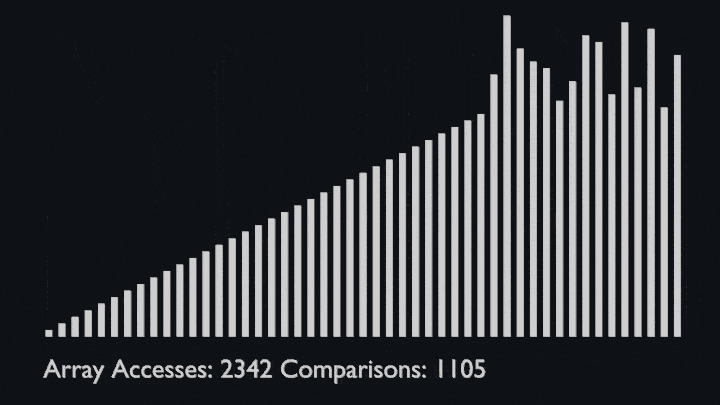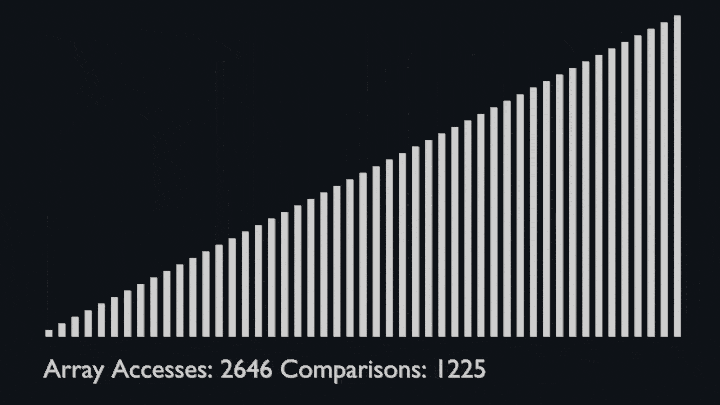
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_scale/selection_sort_scale.py" target="_blank">Script</a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Shell Sort
|
||||
@ -78,7 +82,8 @@ The array is divided into sub-arrays and then insertion sort is applied. The alg
|
||||
<li>Repeat this process until the complete list is sorted.</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
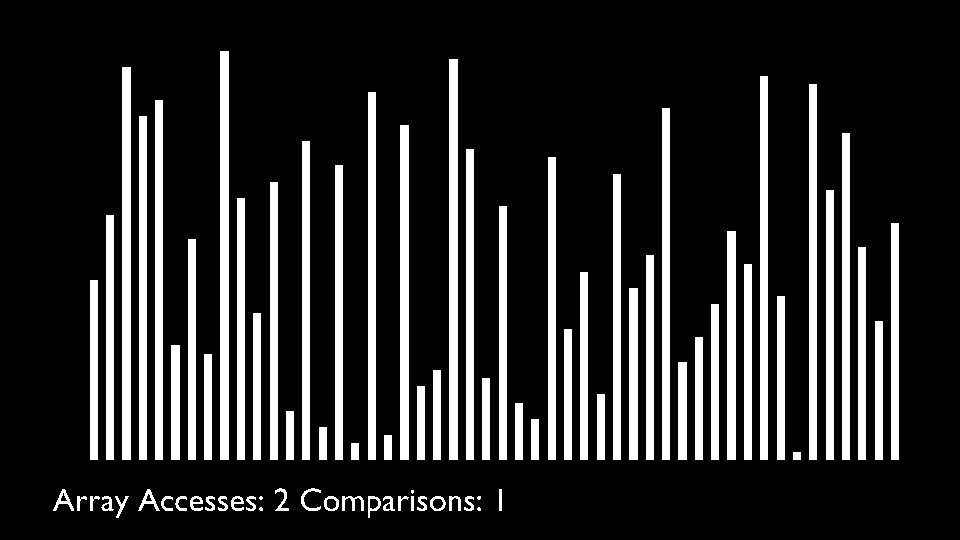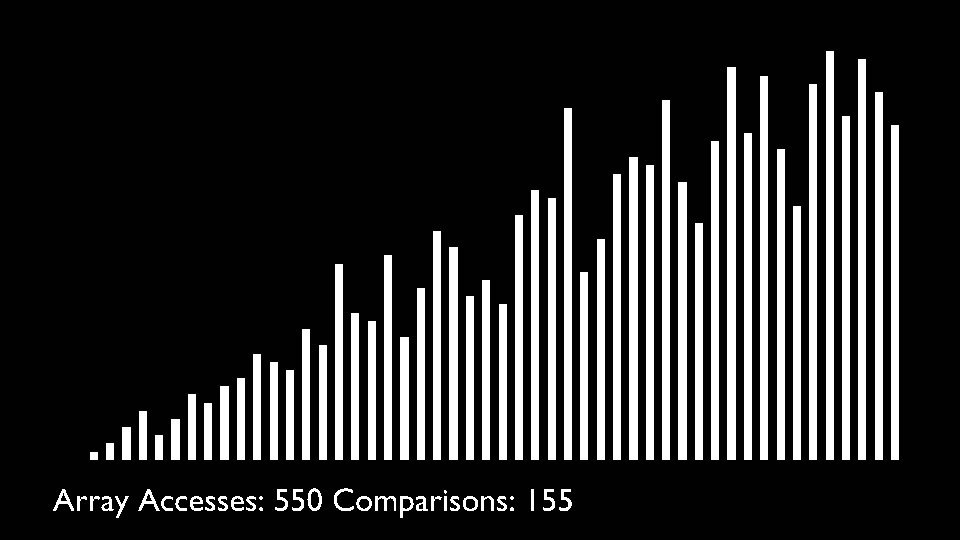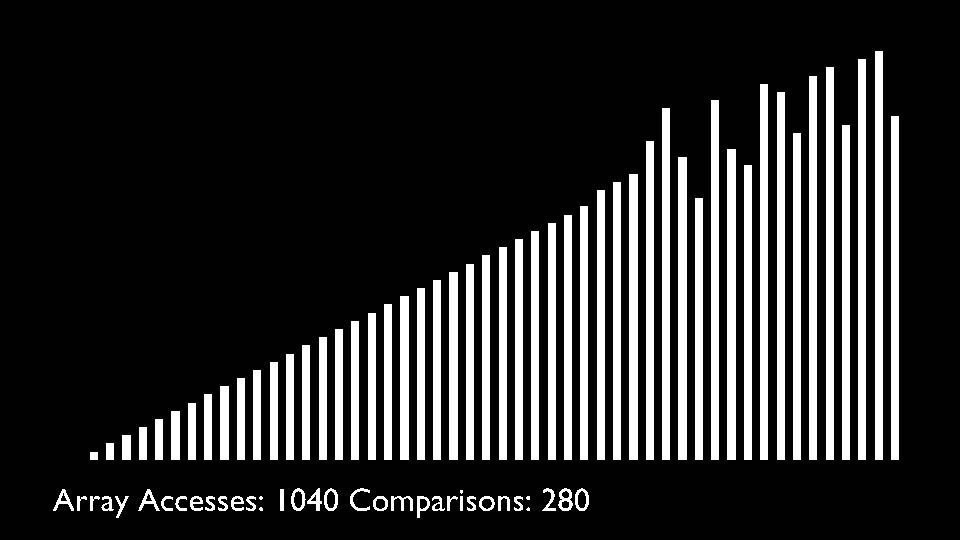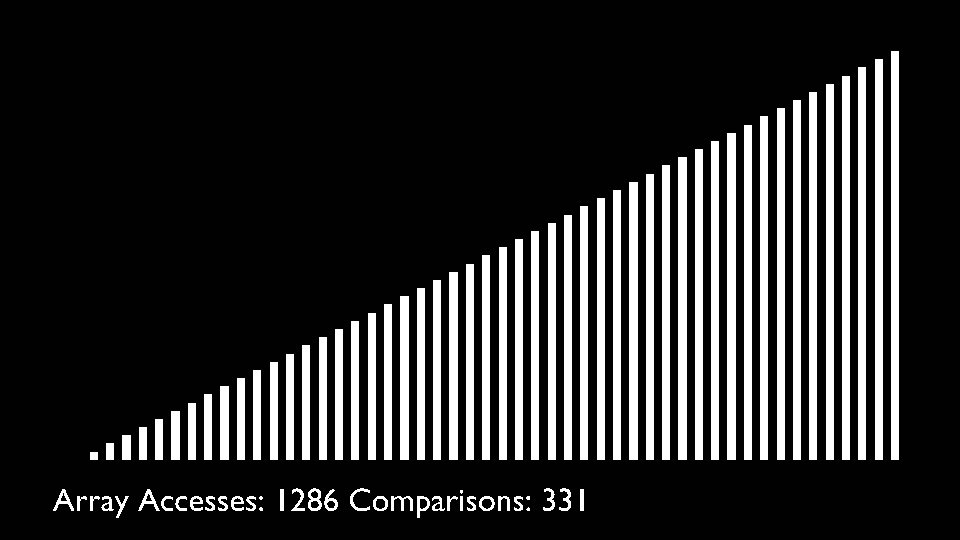
|
||||
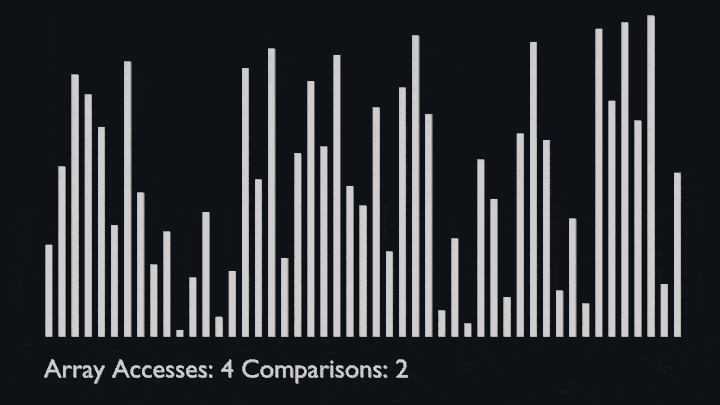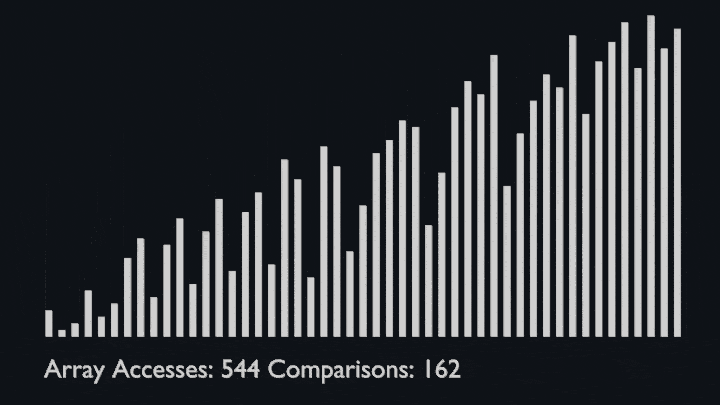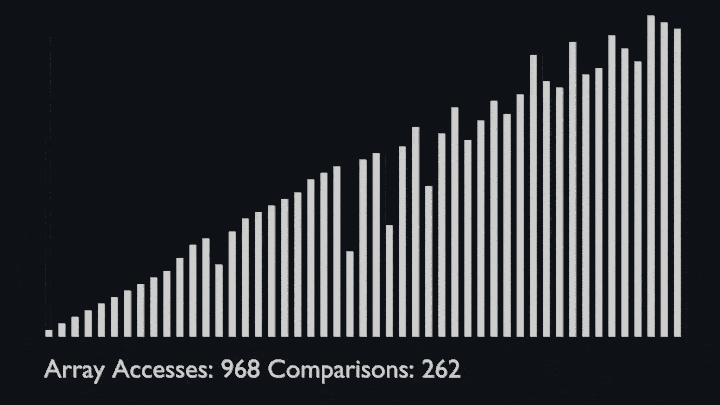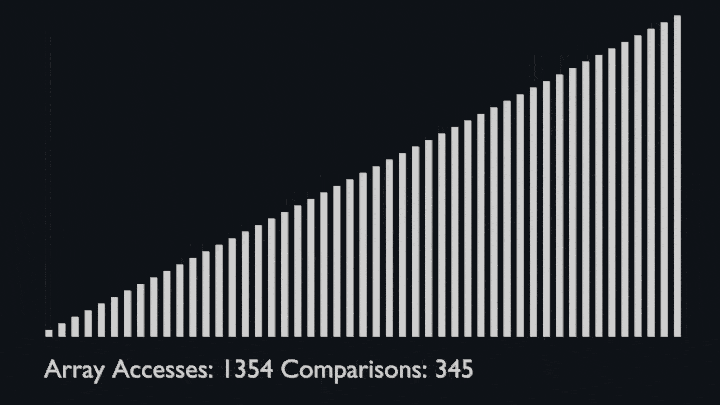
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_scale/shell_sort_scale.py" target="_blank">Script</a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Merge Sort
|
||||
@ -91,6 +96,8 @@ The sub-lists are divided again and again into halves until the list cannot be d
|
||||
Then we combine the pair of one element lists into two-element lists, sorting them in the process.<br>
|
||||
The sorted two-element pairs is merged into the four-element lists, and so on until we get the sorted list.
|
||||
|
||||
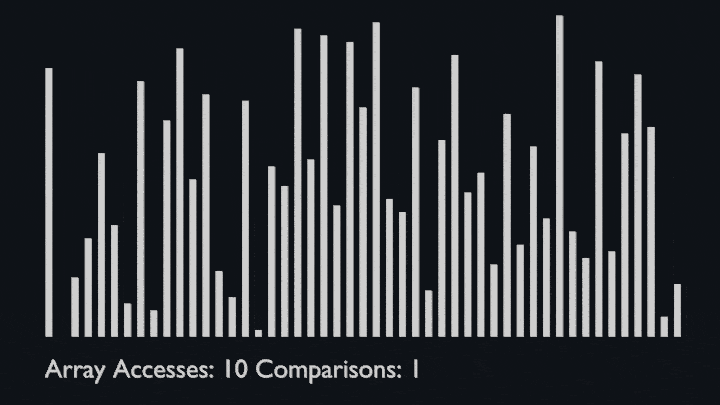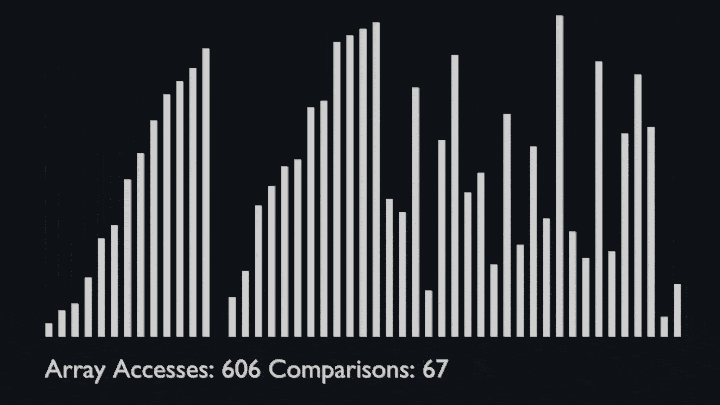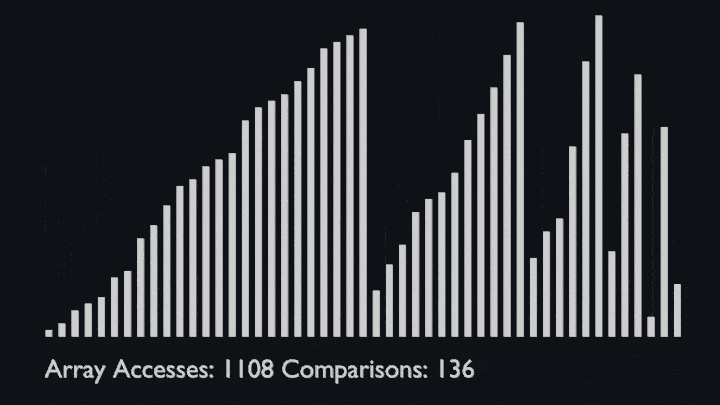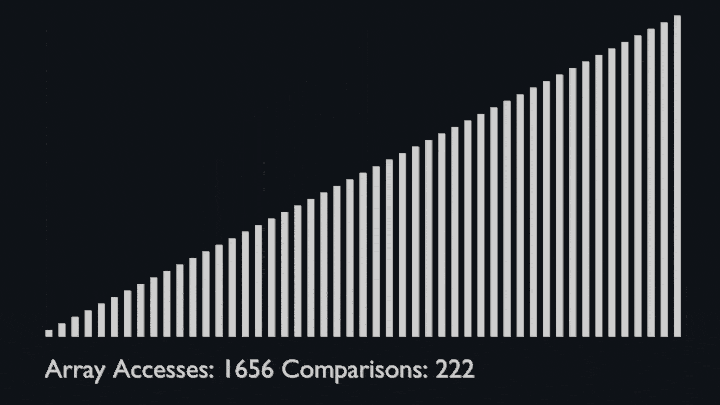
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_scale/merge_sort_scale.py" target="_blank">Script</a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Quick Sort
|
||||
@ -106,7 +113,7 @@ Like Merge Sort, QuickSort is a Divide and Conquer algorithm. It picks an elemen
|
||||
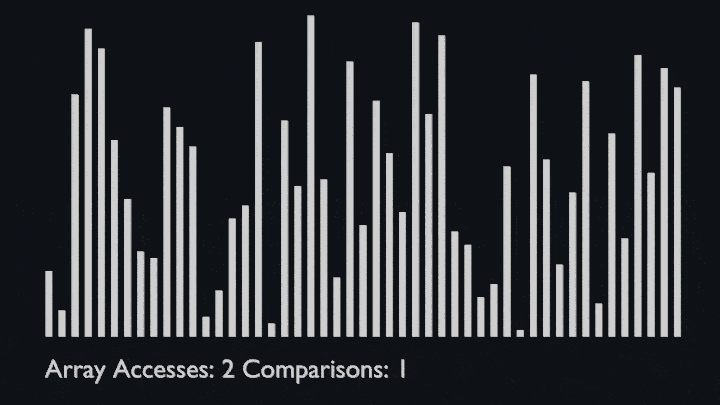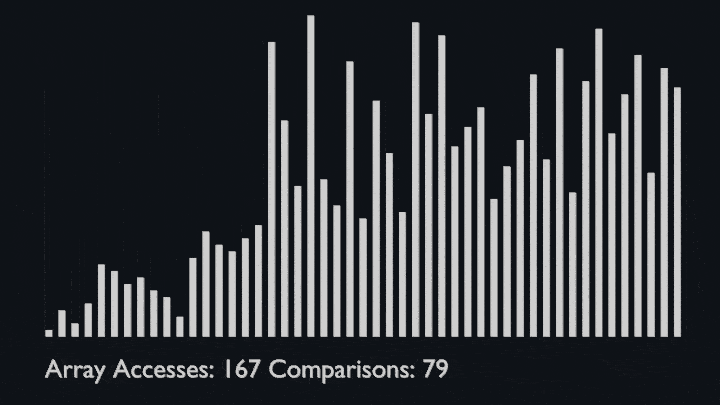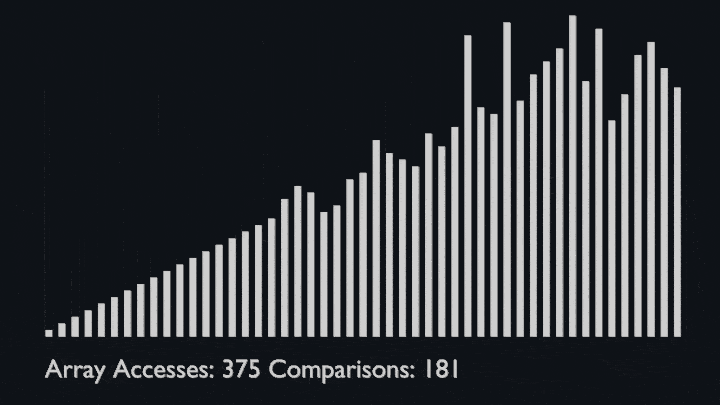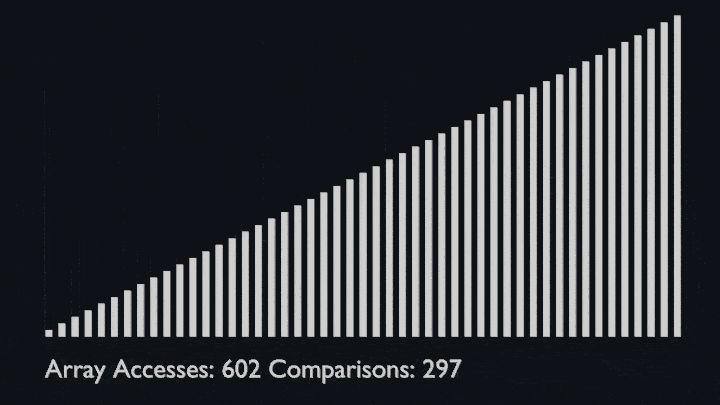
The key process in quickSort is partition(). Target of partitions is, given an array and an element x of array as pivot, put x at its correct position in sorted array and put all smaller elements (smaller than x) before x, and put all greater elements (greater than x) after x.<br>
|
||||
All this should be done in linear time.
|
||||
|
||||
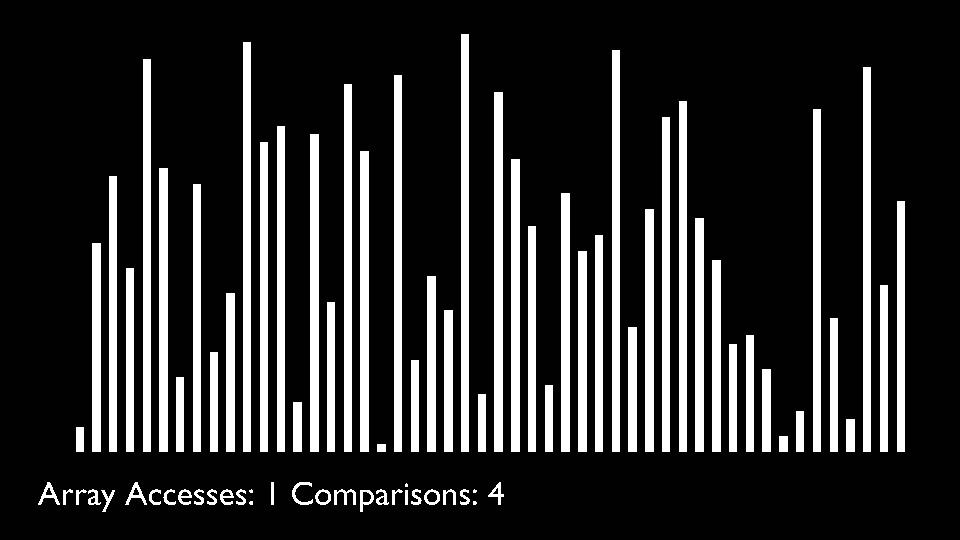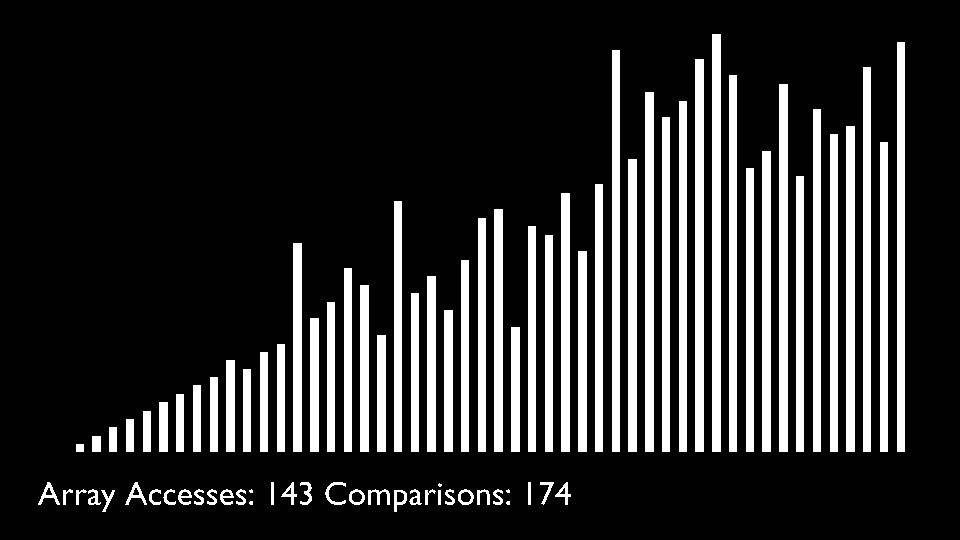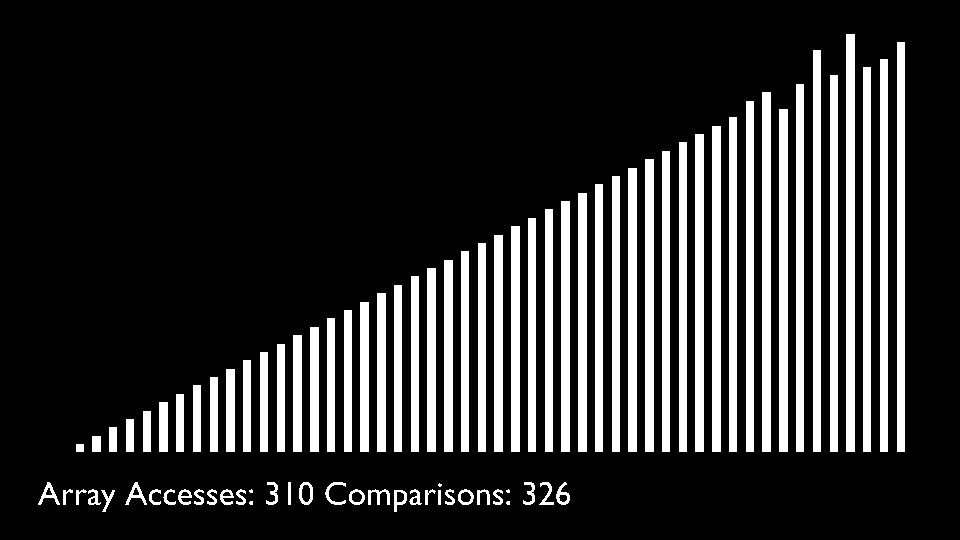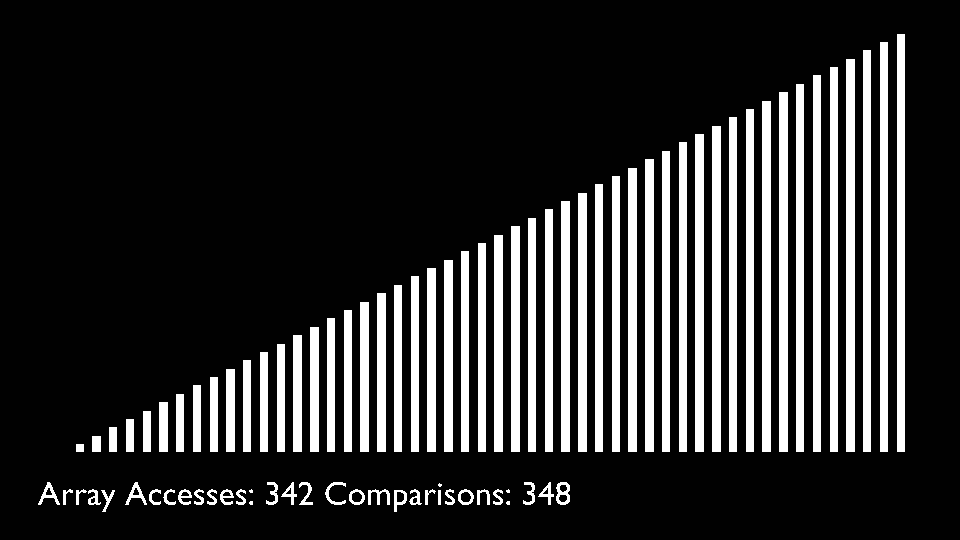
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/ForeignGods/Sorting-Algorithms-Blender/blob/main/sort_scale/quick_sort_scale.py" target="_blank">Script</a>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
x
Reference in New Issue
Block a user